Compression molding is a highly efficient and versatile manufacturing process used to shape materials into a variety of intricate parts. From automotive components to medical devices, this technique allows manufacturers to create durable, high-performance products using a range of materials like rubber, thermosets, silicones, and composites. The article explores the ins and outs of compression moulding, highlighting its applications, benefits, and the materials best suited for this process. Whether you’re designing a custom part or exploring manufacturing solutions, understanding compression molding can significantly enhance your production strategies.
What is Compression Molding?
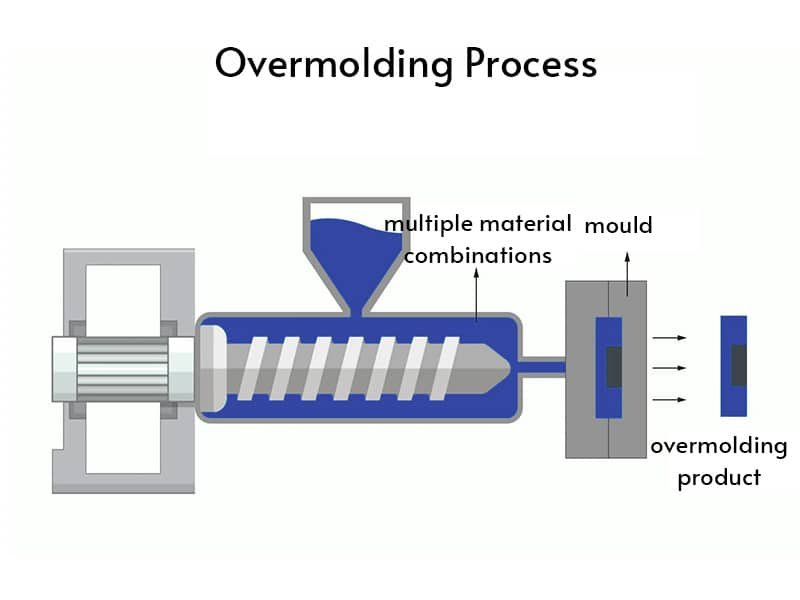
compression forming is a manufacturing process used to shape material into a specified form, particularly in producing rubber, plastics, and silicone components. During the compression moulding process, raw materials are placed into an open mold cavity, which is then closed and heated under pressure. The heat and pressure cause the material to flow, taking the shape of the mold. This method is often used to create high-strength parts, intricate designs, and parts with precise dimensions. The process is widely used in industries that require durable, cost-effective components such as automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.
The Compression Molding Process
- Preparation of Raw Materials: The raw material, usually in the form of pre-measured pellets, powder, or liquid, is chosen based on the application and material properties required for the final product. Common materials include rubber, silicone, and thermosetting plastics.
- Loading the Mold: The material is loaded into the mold cavity, which is specifically designed for the final part. The material is typically placed into the cavity in excess to allow for proper flow during the molding.
- Molding Process: The mold is then closed under pressure, and heat is applied. The combination of pressure and temperature ensures that the material fills the mold cavity entirely. In some cases, the heat can be provided through electrical heating elements, or it can be done through heated plates.
- Cooling: Once the material is fully molded, the mold is cooled to solidify the material. Cooling time varies depending on the material used and the thickness of the molded part.
- Ejection and Finishing: After cooling, the molded part is removed from the mold. It is then inspected for quality and, if necessary, subjected to additional finishing processes such as trimming, grinding, or polishing.
Materials Suitable for Compression Moulding
- Rubber: Rubber is widely used in compression molding due to its flexibility, resilience, and durability. Both synthetic and natural rubbers, such as EPDM and neoprene, are used for products like seals, gaskets, and vibration dampers in automotive and industrial applications.
- Thermosetting Plastics: Thermosetting plastics, like phenolic resins and epoxy, harden when exposed to heat and pressure. These materials are ideal for high-strength, heat-resistant parts like electrical components, automotive parts, and industrial machine housings.
- Silicone: Silicone is known for its heat resistance, flexibility, and non-toxic nature, making it perfect for medical devices, consumer products, and seals. Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) is often used for intricate parts, while solid silicone is used for thicker components.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethane combines the benefits of rubber and plastic, offering flexibility, toughness, and chemical resistance. It’s commonly used for parts like bushings, seals, and gaskets in automotive and industrial sectors.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): TPE materials combine rubber’s elasticity with thermoplastics’ processability. They’re used for high-volume parts requiring flexibility and recyclability, such as in automotive, footwear, and medical industries.
- Fiberglass-Reinforced Composites: Fiberglass composites are used to create strong, durable parts with high mechanical resistance. They’re ideal for products like boat hulls, automotive components, and industrial equipment.
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics (CFRP): CFRP offers high strength and low weight, making it perfect for high-performance applications like aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.
The Benefits of Compression Molding
Compression moulding offers several advantages over other molding techniques, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. Compression molding benefits include:
Cost-Effectiveness
The compression molding process is particularly cost-effective for mass production of large parts or small runs. The mold costs are lower compared to injection molding, making it ideal for both prototyping and high-volume production.
Flexibility with Materials
Compression molding is highly versatile, as it can process a wide variety of materials, including rubber, silicone, and thermosetting plastics. The ability to choose materials based on performance requirements allows manufacturers to produce parts with unique properties, such as high temperature resistance or enhanced flexibility.
Precision and Quality
The process can produce parts with highly precise dimensions. The combination of heat and pressure ensures that material fills the mold completely, resulting in parts with consistent quality and uniformity.
Environmentally Friendly
Since compression molding does not require excessive material usage, it minimizes waste. It also allows for the use of recycled materials in some applications.
Low Energy Consumption
Compared to other molding processes, compression molding typically uses less energy, as the heat is localized and applied directly to the material being molded.
The Applications of Compression Molding
Compression molding is used across many industries, thanks to its adaptability and efficiency. Some key applications include:
Rubber Parts
Compression molding is commonly used to produce rubber parts, such as seals, gaskets, and hoses. These components are essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer products.

Silicone Products
Silicone compression molding is ideal for manufacturing medical devices, seals, and cookware. Its ability to handle high temperatures and provide excellent flexibility makes it perfect for these applications.

Automotive Components
Compression molding technique is common for parts in the automotive industry, automobile parts including bumpers, door seals, and weather stripping, are produced using compression moulding. The process offers the durability and precision required for such critical components.

Electrical Components
Compression molding is used in producing electrical components like connectors, insulators, and switches. These parts must be precise, durable, and capable of handling electrical currents.
Medical Devices
Silicone compression molding is widely used for medical parts such as catheters, seals, and prosthetics. The process ensures that these components meet stringent regulatory requirements while maintaining high precision.

Challenges in Compression Moulding and How to Overcome Them?
While compression molding offers many benefits, it does present a few challenges that manufacturers must navigate:
- Material Flow Issues: In some cases, the material may not flow evenly or fully fill the mold. This can lead to inconsistencies in part quality. To overcome this, manufacturers can adjust the mold design, optimize the material’s viscosity, and carefully control the heating and pressure settings.
- Cycle Time: The cycle time in compression molding can be longer compared to other methods like injection molding, especially when thick or highly detailed parts are involved. This challenge can be mitigated by optimizing mold designs and employing more efficient cooling methods.
- Mold Wear and Tear: Over time, compression molds can wear down, especially when used to process abrasive materials. Regular maintenance, use of durable mold materials, and precise control of the molding process can help prolong the life of the molds.
- Material Variability: Compression molding is highly dependent on the material used. Variations in raw material properties can affect the final product’s quality. Ensuring consistent sourcing of materials and conducting thorough quality control checks is crucial for maintaining consistency.
Best Practices for Successful Compression Molding
To ensure the best results from compression moulding, manufacturers should follow these best practices:
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate material based on the product’s performance requirements. Ensure that it is compatible with the mold and the specific molding process.
- Mold Design Optimization: The mold design should promote uniform material flow and minimize the potential for defects. Features such as vents and proper venting systems can improve molding efficiency.
- Temperature and Pressure Control: Carefully monitor and control the temperature and pressure during the molding cycle to avoid defects such as flashing or uneven material distribution.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance on molds and machinery to prevent defects and ensure long-term efficiency. This includes checking for wear, cleaning, and replacing worn-out components.
- Cycle Time Optimization: Experiment with different cycle times and parameters to find the most efficient settings for the specific material and part design.
Conclusion
Compression molding is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process that is widely used in the production of high-quality parts across multiple industries. Whether it’s rubber, silicone, or thermosetting plastics, the benefits of compression moulding, including its precision, flexibility with materials, and energy efficiency, make it an ideal choice for manufacturing durable components. Despite a few challenges, such as material flow and mold wear, best practices can ensure that manufacturers achieve optimal results. By selecting the right materials and optimizing the process, compression molding provides an excellent solution for creating high-performance parts for applications in automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.