When it comes to manufacturing plastic parts, compression molding vs injection molding is a comparison that many companies face. Both processes are highly effective, but they cater to different production needs, part requirements, and design specifications. The goal of this article is to explore each molding process in-depth, comparing their respective advantages, applications, and helping you understand which method is best for your product manufacturing.
What is Injection Molding?
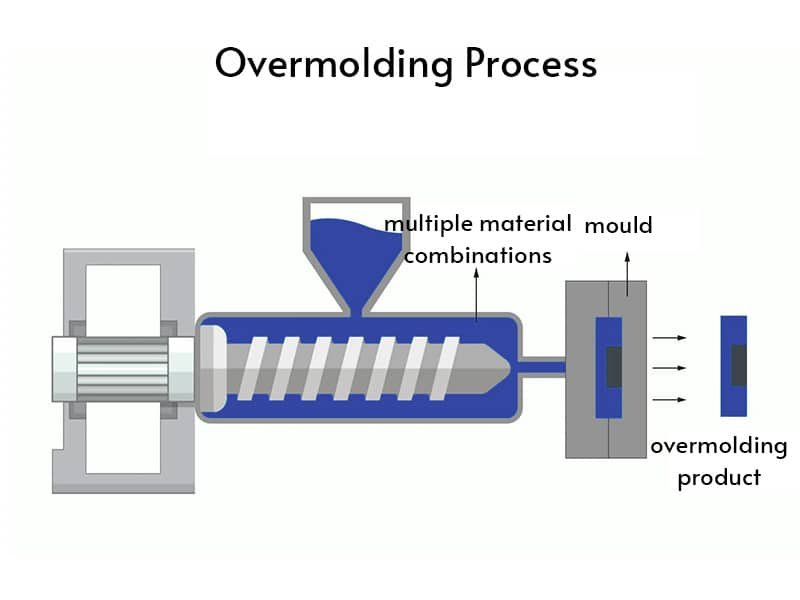
Injection moulding technique is one of the most widely used methods for producing plastic parts. In this process, plastic material, usually in the form of pellets, is melted and injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic fills the cavity and takes the shape of the mold. After cooling and solidifying, the part is ejected. This method is highly efficient, suitable for high-volume production, and produces parts with excellent detail and dimensional accuracy.
The key advantages of injection molding include its ability to produce intricate shapes, high repeatability, and rapid production rates. It is often used for manufacturing small, complex parts like connectors, enclosures, and consumer goods components.

What is Compression Molding?
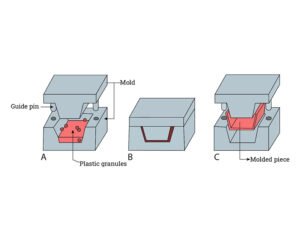
Compression molding is another popular method for producing plastic parts, but the process differs significantly from injection molding. In compression moulding, a pre-measured amount of material (typically thermosetting plastics or rubber) is placed in an open, heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to shape the material. The part is allowed to cure (harden) while under pressure, and once it cools, it is ejected from the mold.
Compression moulding is best suited for large parts or components that require high durability and strength, such as automotive parts, seals, gaskets, and electrical insulations. It also allows for the use of both thermosets and thermoplastics.
Similarities between Compression Molding vs Injection Molding
Despite their differences, injection molding and compression molding share several similarities. Both processes involve the use of molds to form the material into specific shapes. Both rely on heating and applying pressure to form the material into the desired shape, and both processes produce high-precision, repeatable results.
Additionally, both methods are highly automated, leading to consistent output with minimal human intervention. The primary materials used in both processes include plastics, though each process is optimized for specific types of plastics or composites.
Differences between Injection Molding and Compression Molding
1. Material Type and Preparation
One of the key differences between compression vs injection molding is the type of materials used. Injection molding typically uses thermoplastics, which can be melted and molded multiple times without altering the material properties. In contrast, compression molding often uses thermosetting plastics or rubber. These materials harden when cured and cannot be re-melted once processed.
2. Molding Process and Equipment
In injection molding, the process starts with heating plastic pellets until they are molten, and the material is then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. This allows the process to produce parts with intricate features and tight tolerances.
On the other hand, compression moulding involves placing a pre-measured amount of material into the mold, where it is heated and compressed under pressure. This results in simpler, often larger parts with less intricate detailing.
3. Tooling Costs
The tooling cost is another key point of distinction. Injection molding tools are generally more expensive to manufacture than compression molding tools. Injection molds require more precision and are usually made from high-quality steel, making them more costly to produce. In contrast, compression molds can be made at a lower cost due to their simpler designs and materials.
4. Cycle Time
Injection molding tends to have faster cycle times because the material is already preheated, and the pressure required to fill the mold cavity is applied quickly. In contrast, compression molding can take longer as the material needs time to cure and cool in the mold.
5. Part Complexity
Injection molding excels at producing complex parts with fine details and high precision, which makes it ideal for producing intricate geometries. Compression molding, on the other hand, is better suited for simpler, larger parts where high strength is a priority.
6. Production Volume
Injection molding is particularly advantageous for high-volume production due to its rapid cycle times and ability to produce large quantities of parts quickly. Compression moulding is more commonly used for medium to low-volume production, though it still offers good efficiency for specific types of parts.
How to Choose Between Injection Molding and Compression Molding?
Choosing the right molding process depends on several factors such as part design, material requirements, production volume, and budget. Here are some factors to consider when deciding between injection molding and compression molding:
1. Part Design and Complexity
If your product has intricate features or requires high precision, injection molding is likely the better choice. The process allows for finer detailing and is well-suited to producing parts with thin walls, complex geometries, and tight tolerances. If your part is larger and requires a simpler shape, compression molding may be a better option.
2. Material Requirements
Consider the material needed for your part. Injection molding is ideal for thermoplastics, especially those that need to be reprocessed, while compression moulding works best with thermosetting plastics, rubber, and certain composite materials. If your part requires a material that hardens during the process and cannot be re-melted, compression molding is the more suitable choice.
3. Production Volume
For large-scale production runs, injection molding is generally more cost-effective due to its faster cycle times and ability to produce large quantities of parts in a short period. For medium to small production volumes, compression moulding may be more practical due to its lower tooling costs and suitability for specific part types.
4. Budget and Tooling Costs
If tooling costs are a major consideration, compression molding may offer a more cost-effective solution. The molds required for compression molding are typically simpler and less expensive to manufacture, making it a better choice for low-cost manufacturing. However, if you need highly intricate, precise parts, investing in injection molding tooling may be worthwhile in the long run.
Conclusion
In the debate of compression molding vs injection molding, both processes have their merits and are suited to different applications. Injection molding is ideal for high-precision, high-volume production of complex parts, while compression moulding excels in manufacturing larger, simpler parts with durable materials. Understanding the unique features and advantages of each method will allow you to make an informed decision about the best molding process for your product. Whether you’re manufacturing consumer products, automotive parts, or industrial components, both injection molding and compression molding offer versatile solutions for plastic parts manufacturing.