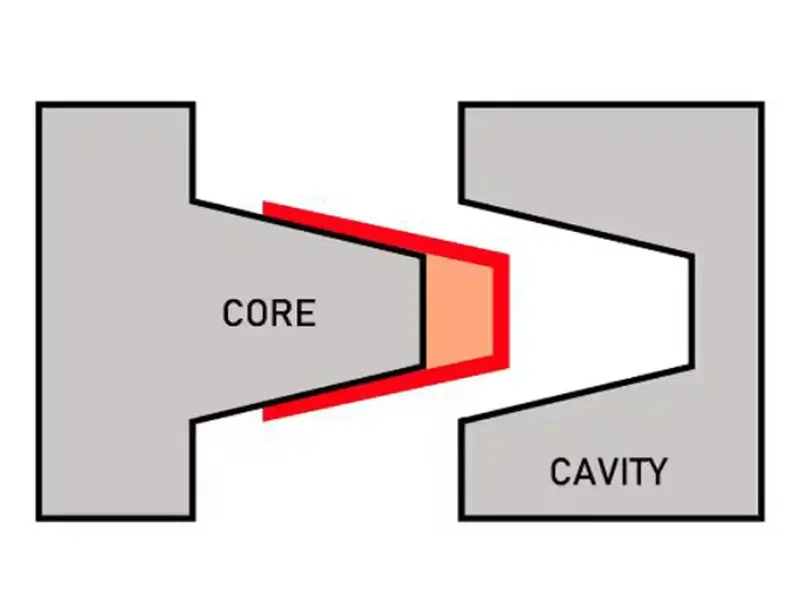
The injection mold cavity is the heart of the injection molding process, defining the outer shape and surface finish of the final product. Whether you’re designing a mould cavity for a simple part or a multi cavity mold for mass production, understanding the intricacies of cavity molding is essential. From core and cavity in mould design to creating a cavity in Solidworks, this guide covers everything you need to know to optimize your injection mold cavity for efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.

What is an Injection Mold Cavity?
The injection mold cavity (or mould cavity) is the negative space within the mold where molten plastic is injected to form the outer shape of the part. It works in tandem with the core cavity to create the complete structure of the molded item. The core and cavity in mould design must be precise to ensure proper part formation, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy.
Key Function: The injection mold cavity defines the external features of the part, while the core shapes the internal features. Together, they ensure the final product meets design specifications.
Core and Cavity in Mould: Key Differences
Injection Mold Cavity: Forms the outer surface of the part. It is typically stationary and must withstand high injection pressures.
Core Cavity: Forms the inner surface or internal features of the part. It is often movable to facilitate part ejection.
Design Tip: Proper alignment between the core cavity and injection mold cavity is critical to avoid defects like flash or misalignment.
Types of Injection Mold Cavities
Understanding the different types of mold cavities is essential for selecting the right mold design based on production needs and efficiency. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Single Cavity Molds
- Best for: Low-volume production, prototyping, or highly complex parts.
- Advantages: Easier to design and maintain, ideal for cavity molding of custom parts.
- Disadvantages: Lower production efficiency compared to multi cavity mold designs.
Multi-Cavity Molds
- Best for: High-volume production of identical parts.
- Advantages: Higher efficiency and lower cost per part.
- Disadvantages: Requires careful design to ensure uniform filling across all cavities.
Family-Cavity Molds
- Best for: Producing different but related parts in a single cycle.
- Advantages: Reduces the need for multiple molds.
- Disadvantages: Design complexity and potential for unbalanced filling.
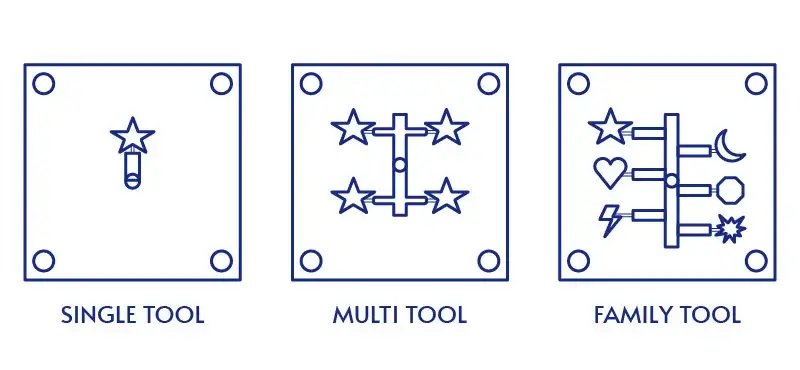
Single-Cavity Mold vs Multiple-Cavity Mold vs Family-Cavity Type
| Feature | Single Cavity | Multi-Cavity | Family-Cavity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Low to medium | High | Small to medium |
| Efficiency | One part per cycle | Multiple identical parts per cycle | Different related parts per cycle |
| Part Complexity | Complex designs possible | Simpler, standardized designs required | Some design variations possible |
| Design Flexibility | High | Low | Medium |
| Tooling Costs | Lower | Higher | Higher than single cavity |
| Cost per Part | Higher | Lower | Medium |
| Lead Time | Shorter | Longer | Longer than single cavity |
| Suitable Applications | Prototyping, low-volume production of complex parts | High-volume production of standardized parts | Small to medium production runs of related components |
Designing an Injection Mold Cavity in Solidworks
Creating a cavity in Solidworks involves:
- Importing the part design into Solidworks.
- Using the Cavity Tool to generate the negative space for the mold.
- Adding features like cooling channels, ejector pins, and gates.
- Simulating the injection process to ensure even filling and cooling.
Pro Tip: Use Solidworks’ simulation tools to test for potential issues like air traps or uneven cooling before manufacturing the mold.
How to Choose the Right Injection Mold Cavity ?
When selecting between single cavity, multi cavity mold, or family cavity designs, consider:
- Production Volume: High-volume production benefits from multi cavity mold designs.
- Part Complexity: Complex parts may require a single cavity mold for better control.
- Cost: Multi cavity molds have higher upfront costs but lower cost per part.
- Lead Time: Single cavity molds are faster to design and manufacture.
Common Challenges in Injection Mold Cavity Design
- Air Traps: Caused by poor venting in the injection mold cavity.
- Uneven Filling: Often due to improper gate placement or unbalanced multi cavity mold designs.
- Part Defects: Misalignment between core and cavity in mould can lead to flash or dimensional inaccuracies.
Solution: Regular maintenance, proper venting, and simulation testing can mitigate these issues.
Optimizing Injection Mold Cavity Design for Quality and Efficiency
Material Selection: Use high-quality mold steel for durability.
Cooling Channels: Design efficient cooling channels to reduce cycle time.
Venting: Ensure proper venting to avoid air traps.
Simulation: Use tools like Solidworks to simulate the cavity molding process before production.
Conclusion
The injection mold cavity is a critical component in injection molding course, directly impacting part quality, production efficiency, and cost. Whether you’re designing a single cavity mold for prototypes or a multi cavity mold for mass production, understanding the nuances of core and cavity in mould design is essential. By leveraging tools like cavity in Solidworks and following best practices for cavity molding, you can optimize your injection mold cavity for high-quality, defect-free parts.