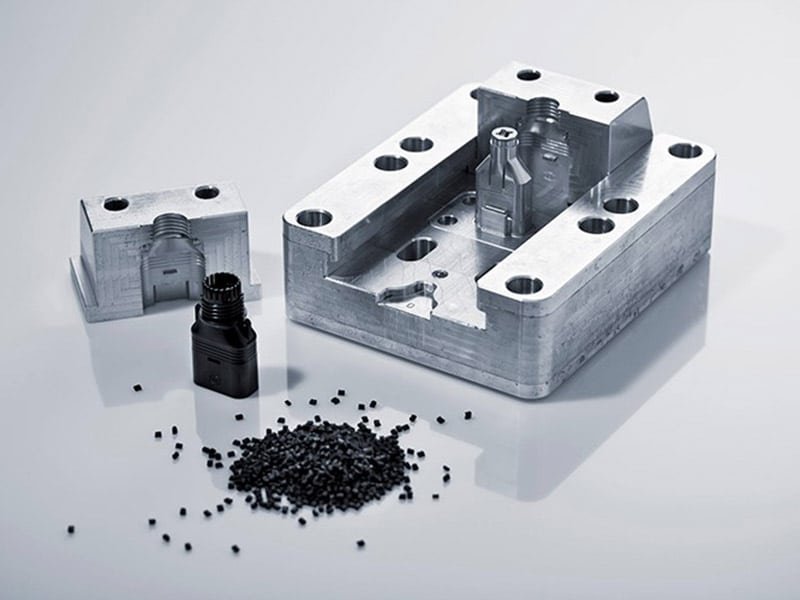
Injection mold making is a fundamental process in manufacturing plastic parts with precision, consistency, and speed. This guide dives into everything you need to know about the process, from the mold structure and design to material choices, cost factors, and quality control.
What is Injection Mold Making?
Injection mold making is the process of designing and manufacturing a mold used in injection molding—a manufacturing technique where molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity to form a part. This process is widely used for producing large volumes of consistent and complex plastic components.
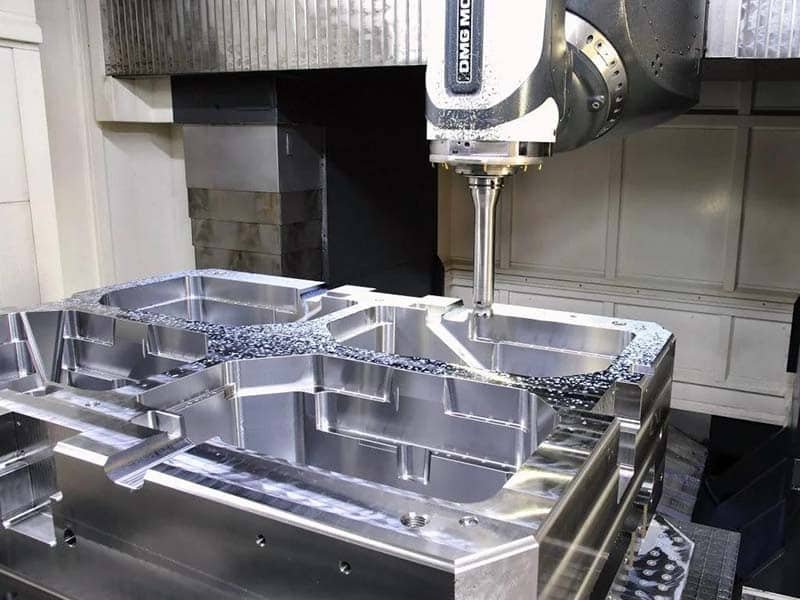

Key Components of an Injection Mold
Understanding mold structure is crucial for both designers and manufacturers. A typical injection mold consists of:
- Cavity and Core: The main forming parts of the mold that shape the plastic.
- Runner and Gate System: Channels through which plastic flows into the cavity.
- Cooling System: Ensures the mold cools uniformly and efficiently.
- Ejection System: Removes the molded part from the mold once it solidifies.
- Support Plates and Guide Pins: Provide structural integrity and alignment.
Types of Injection Molds
There are several types of molds, each serving different purposes in plastic injection molding:
Single-Cavity Mold: This mold creates one part per cycle. It’s ideal for simple parts or lower production volumes.
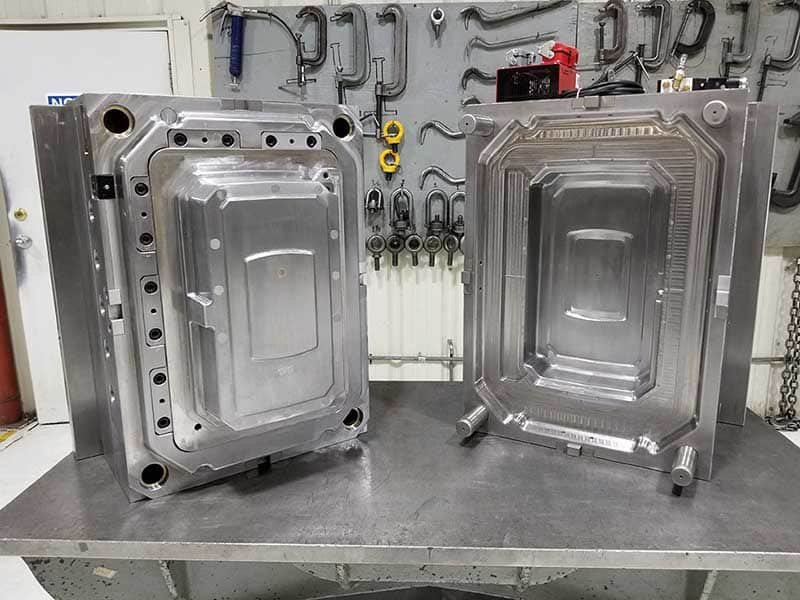

Multi-Cavity Mold: Designed to produce multiple parts per cycle, these molds increase production efficiency and reduce per-part costs for high-volume runs.
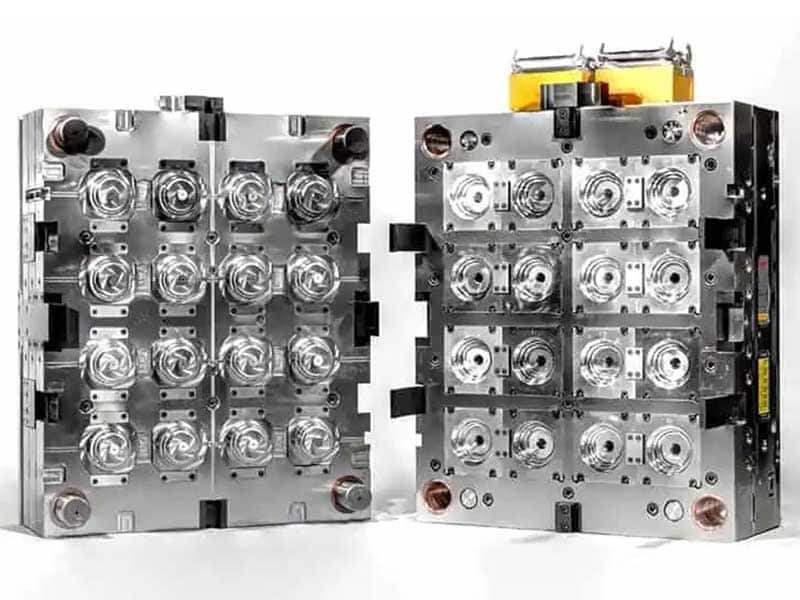
Hot Runner Molds: These molds maintain molten plastic within the system, reducing waste and improving cycle time efficiency.
Cold Runner Molds: The opposite of hot runner molds, cold runner molds rely on the plastic cooling in the runner system, making them suitable for shorter production runs or parts requiring lower precision.

Cold & Hot Runner Injection Mold
The Methods of Injection Mold Making
Injection mold making involves various techniques, each tailored to specific production needs. The method chosen can influence cost, precision, and production time.
Traditional Mold Making
Traditional mold making uses manual techniques like milling, grinding, and drilling to create molds. While it’s ideal for low to medium-volume runs, it is time-consuming and costly for complex parts.
CNC Machining
CNC machining automates mold creation, improving precision and speed. This method is highly efficient for complex molds and ensures consistent quality, making it one of the most popular techniques in modern mold making.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is used for rapid prototyping and low-volume production. It offers faster turnarounds and cost-effective solutions for testing mold designs, though it’s less durable compared to metal molds.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping accelerates the design and testing of molds. This method allows for quick iterations and adjustments, helping manufacturers address potential issues before full-scale production begins.
Step-by-Step Mold Making Process
- Design & DFM Analysis: CAD modeling and manufacturability review.
- Mold Flow Analysis: Simulates plastic flow to optimize gate location and cooling.
- Material Selection: Based on part requirements and mold longevity.
- Machining: CNC and EDM processes shape the mold.
- Assembly: Components are assembled into a working mold.
- Trial & Tuning: Test shots ensure the mold produces accurate parts.
- Validation & Delivery: Final inspection and shipping.Injection Mold Making Process Injection Mold Making Process

Molds Material Selection Guide
Choosing the right material for the mold is key to performance and cost-effectiveness:
- P20 Steel: Pre-hardened, suitable for medium production.
- 718 Steel: Excellent polishability, used for clear parts.
- NAK80: Pre-hardened, good for cosmetic finishes.
- H13 Steel: High wear resistance, ideal for high-volume runs.
- S136 Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, for medical/optical applications.
- Aluminum: Quick machining, good for prototyping or low volume.
- Beryllium-Copper: Used for inserts requiring rapid heat transfer.
Design Considerations for Injection Molds
Mold design plays a crucial role in the efficiency of the injection molding process. Some important design considerations include:
- Part Geometry: The complexity of the part geometry directly influences the design of the mold. Sharp corners, deep cavities, or intricate shapes may require special modifications in the mold structure.
- Draft Angles: Draft angles are sloped surfaces that facilitate the removal of the part from the mold. The inclusion of these angles ensures that parts are ejected smoothly and without damage.
- Wall Thickness: Consistent wall thickness ensures uniform material flow and helps avoid defects such as sink marks and warping.
Mold Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring the mold performs correctly involves rigorous quality procedures:
- Material Inspection: Verify hardness and specifications.
- Dimensional Checks: CMM machines and 3D scanning verify accuracy.
- Trial Molding: Evaluate molded samples for flash, warping, or short shots.
- Final Mold Qualification: Includes production-ready testing and documentation.
Factors Affecting Plastic Injection Mold Making Cost
Mold cost varies widely depending on:
- Part Complexity: More intricate parts require more complex tooling.
- Number of Cavities: Multi-cavity molds are more expensive but increase output.
- Mold Size & Material: Larger molds and premium materials cost more.
- Precision & Tolerance: Tight tolerances increase machining cost.
- Surface Finish Requirements: High polish or texture adds to cost.
- Cooling & Cycle Time Design: Efficient cooling improves productivity but may add complexity.
Tips to Reduce Mold Cost:
- Simplify part design
- Use standardized mold bases
- Optimize gate and cooling layout early
Importance of Mold Maintenance and Care
Proper mold repair and maintenance are essential for maintaining consistent part quality and ensuring long-term efficiency. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection can prevent mold wear, and repairs should be made promptly to avoid delays in production.
Why Choose Jiangzhi Injection Mold Making Services?
Since 1978, we’ve specialized in mold design and manufacturing with decades of experience and state-of-the-art facilities. We offer:
- One-stop solutions: From design to finished mold
- Advanced software & equipment: CAD/CAM, mold flow analysis, precision CNCs
- Material flexibility: Support for a wide range of mold steels and inserts
- Strict quality control: ISO standards, full documentation
- Fast lead times: Streamlined project management for on-time delivery
Conclusion
Injection mold making is a cornerstone of plastic part manufacturing. With the right partner, you can ensure quality, durability, and efficiency. Whether you’re producing a prototype or scaling up to millions of parts, mold design and build quality will define your success.



