OEM vs Contract Manufacturing, the choice between the two services is a critical decision for businesses across industries. Understanding the nuances of these two approaches is essential for making informed decisions that align with your company’s objectives and requirements.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) is an integral player in the production process, often designing and producing components or products under their brand name. They typically handle all aspects of production, from design and engineering to manufacturing and distribution. In contrast, contract manufacturers specialize in providing manufacturing services to businesses that require external expertise and resources. They offer flexible solutions tailored to the specific needs of their clients, allowing companies to outsource certain aspects of their production process.
In this blog, we will explore these distinctions and help you understand OEM vs contract manufacturing, the difference between them. You can navigate the manufacturing landscape more effectively and choose the approach that best suits your needs.
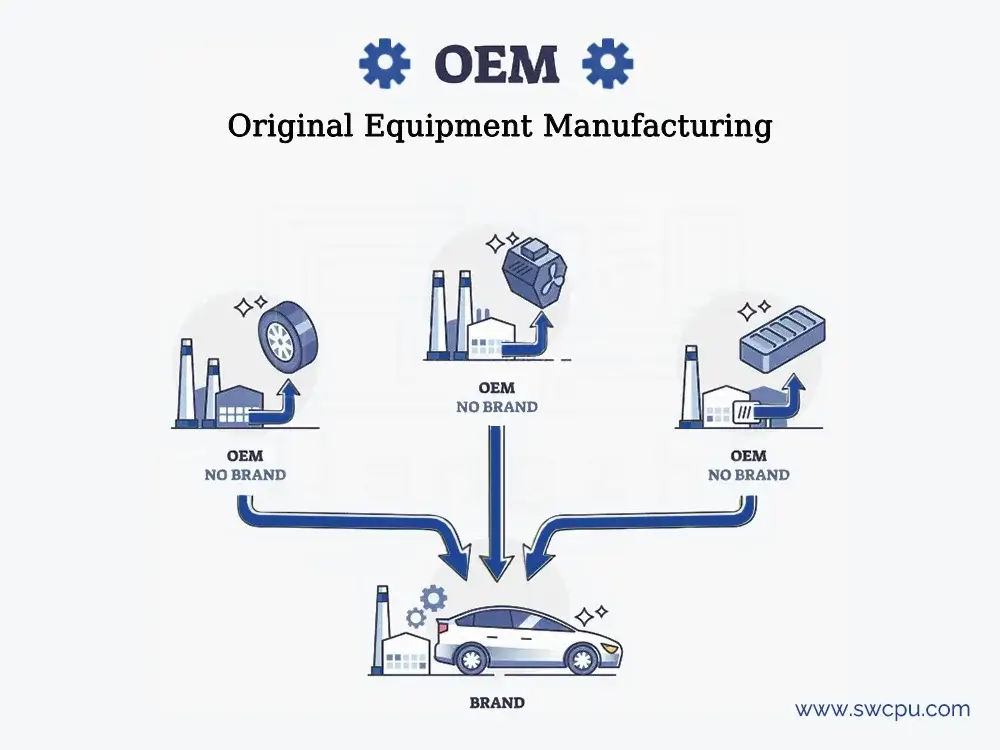
What is OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing)?
An Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) is a company that produces components or products that another company sells under their brand name. OEM manufacturers typically specialize in designing and manufacturing specific parts or products according to the specifications provided by the brand owner. This allows the brand owner to focus on marketing and selling the product without having to invest in manufacturing facilities or capabilities. OEM manufacturers often work closely with the brand owner to ensure that the products meet their quality standards and requirements.
The work with an OEM company starts with an initial consultation where the client discusses their product requirements with the OEM company. Then, the OEM company may assist in designing and developing the product, creating prototypes for testing. Once the design is finalized, a manufacturing agreement is drafted, outlining terms and costs. Production begins according to the agreed specifications, with the OEM implementing quality control measures throughout. Finally, the finished products are delivered to the client, who may also receive post-sales support from the OEM company.
Advantages of Cooperating with OEM Company
OEM vs contract manufacturing, working with an OEM company offers several advantages to contract manufacturing. Some of these are:
- OEM companies specialize in manufacturing specific components or products, bringing expertise and experience to the production process.
- By outsourcing manufacturing to an OEM, companies can avoid the costs associated with setting up and maintaining their manufacturing facilities.
- OEMs can scale production according to demand, allowing companies to meet fluctuating market needs without investing in additional resources.
- Focus on core competencies: Outsourcing manufacturing to an OEM allows companies to focus on their core competencies such as product development, marketing, and sales.
Disadvantages of Cooperating with OEM Company
When compare OEM vs contract manufacturing, working with an OEM company also has disadvantages, including:
- Less control over the manufacturing process and quality control may lead to potential issues with product consistency and quality.
- Most OEM companies often require higher minimum order quantities (MOQs), this can be cost-prohibitive, especially for smaller projects with limited budgets.
- Sharing proprietary designs, or other sensitive information with an OEM manufacturer may pose a risk of intellectual property theft.
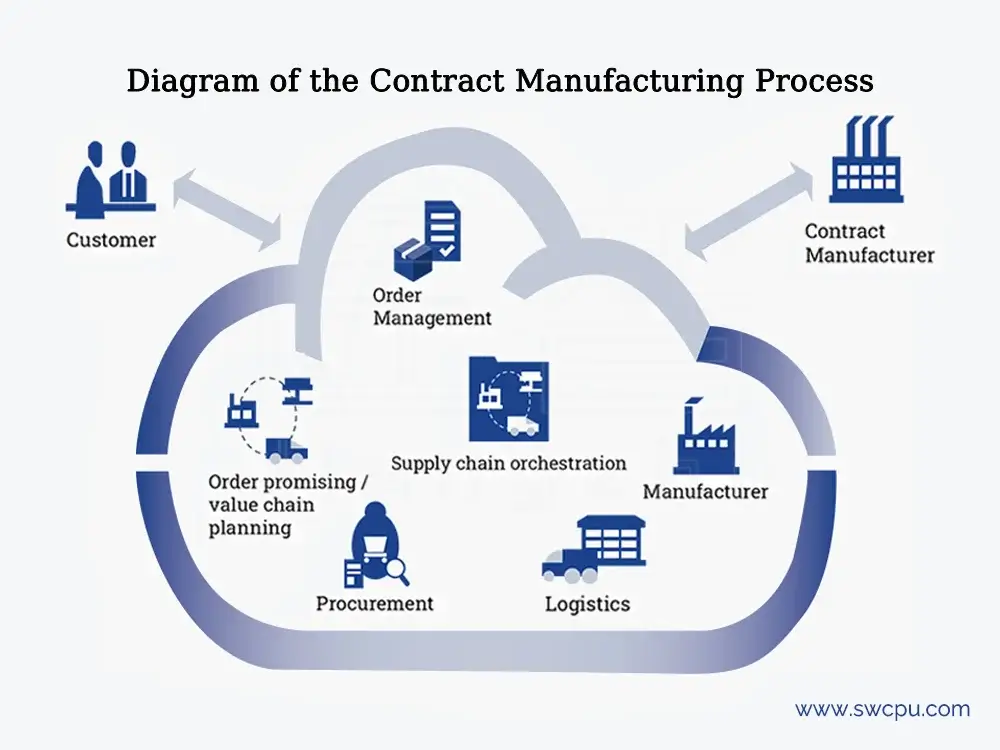
What is a Contract Manufacturer?
A contract manufacturer is a company that produces goods on behalf of another company, known as the “brand owner” or “contracting company”. Contract manufacturers manufacture products according to the specifications, designs, and requirements provided by the brand owner. Contract manufacturers often specialize in specific manufacturing processes or industries and offer their manufacturing services to companies looking to outsource production. They handle various aspects of the manufacturing process, including sourcing raw materials, production, quality control, and sometimes even packaging and distribution.
The cooperation begins with the brand owner providing detailed specifications, designs, and requirements for the product to be manufactured. The contract manufacturer then evaluates the feasibility of the project. Once both parties agree on terms, such as pricing, production timelines, and quality standards, the contract manufacturer proceeds with sourcing raw materials, setting up production lines, and manufacturing the products.
Throughout the production, the brand owner may collaborate closely with the contract manufacturer to ensure that the products meet their quality standards and requirements. After production, the contract manufacturer may also assist with packaging, labeling, and shipping the products to their final destination.
Advantages of Cooperating with Contract Manufacturers
OEM vs contract manufacturing, working with a contract manufacturer offers several advantages to OEMs. Some of these are:
- Contract manufacturers can quickly adjust production levels to meet fluctuating demand, allowing brands to scale production without significant investment.
- Contract manufacturers can accommodate variable production volumes and timelines, providing greater flexibility for brands.
- Mitigate risks such as capital investment, equipment maintenance, and labor management.
- The clients often retain ownership of the design’s intellectual property (IP), ensuring control and security.
Disadvantages of Cooperating with Contract Manufacturers
When compare OEM vs contract manufacturing, working with a contract manufacturer also has disadvantages, including:
- Clients may have less control over the manufacturing process and quality assurance.
- Contract manufacturers may experience production delays due to various factors such as capability constraints, equipment malfunctions, or supply chain disruption
- Contract manufacturing often involves the development of tooling and products from scratch, which can result in longer project lead times.
OEM vs Contract Manufacturing, What are the Differences?
Customer Involvement
OEM:
OEMs typically have less direct customer involvement as they focus on producing products based on provided specifications, offering limited flexibility for customization.
Contract Manufacturer:
Contract manufacturers engage more directly with customers, collaborating closely to develop designs, select materials, and customize production processes to meet specific needs, offering greater flexibility and adaptability.
Initial Investment in Product Development
OEM
OEM manufacturers, or Original Equipment Manufacturers, often require a substantial initial investment in product development. This is because they are responsible for creating the product from scratch, involving extensive design, prototyping, and testing processes.
Contract Manufacturer
contract manufacturers typically have existing infrastructure, resources, and expertise in place to produce a wide range of products for various clients, so clients don’t need to invest as much upfront.
Time to Market
OEM
OEM manufacturers, being responsible for the entire product lifecycle, tend to have longer time to market. They handle all stages, including design, prototyping, testing, and production, which can result in a more extended development timeline.
Contract Manufacturer
Contract manufacturers, specializing in production, can expedite the time to market significantly. Since they focus solely on manufacturing, they have streamlined processes and infrastructure in place, allowing for quicker turnaround times and faster product launches.
Manufacturing Flexibility
OEM
OEM manufacturers may face limitations in manufacturing flexibility due to their commitment to producing specific products under a brand name. They are often focused on mass production of standardized products, which can restrict their ability to adapt quickly to changing market demands or customize products for different clients.
Contract Manufacturer
Contract manufacturers typically offer greater manufacturing flexibility. They are accustomed to working with a variety of clients and product specifications, allowing them to adjust production processes, scale production volumes, and accommodate customizations more readily.
IP Right, the Ownership and Branding
OEM
OEM manufacturers usually retain ownership of the intellectual property (IP) rights for the products they produce. They develop and market products under their brand names, leveraging their brand reputation to attract customers. But this can be negotiated in the contract.
Contract Manufacturing
Contract manufacturers typically do not own the IP rights for the products they produce. They manufacture products according to the specifications provided by their clients, who retain ownership of the IP rights. They may produce goods under their clients’ brands or provide white-label manufacturing services.
Choosing the Right Type of Manufacturing Service
Businesses can make informed decisions when choosing between OEM and contract manufacturing, following factors should be carefully considered.
- Level of IP sensitivity: If your product’s intellectual property (IP) is mainly about its design and basic features, go with OEM. But for products with complex IP, like custom software or innovative functions, contract manufacturing offers better IP protection.
- Project budget: OEMs typically have lower initial investment costs, while CM require new designs and tooling, resulting in higher investment costs. When budgets for development or tooling are limited, OEMs are generally the preferred choice.
- Production volume: OEM is suitable for high-volume production, while contract manufacturing is flexible for both low and high volumes.
- Supply chain management: OEM involves managing multiple suppliers, while contract manufacturing streamlines the supply chain through a single partner.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision between OEM vs contract manufacturing hinges on various factors including customer involvement, initial investment, time to market, IP rights, and cost considerations. While OEMs offer greater control over product development and branding, contract manufacturers provide flexibility, expertise, and cost advantages. Ultimately, the choice depends on the specific needs, resources, and goals of the company. As a injection molding contract manufacturer, Jiangzhi can help you overcome challenges in your molding services and ensure high-quality production.