Urethane casting has become a pivotal technique in manufacturing, offering a cost-effective, versatile, and efficient solution for creating high-quality prototypes and low-volume production parts. This process involves the use of liquid urethane poured into flexible molds, enabling manufacturers to replicate detailed designs with exceptional precision. Whether you are looking to develop a prototype, create custom components, or test material properties, urethane casting provides a rapid alternative to traditional methods like injection molding. This article explores the fundamentals of urethane casting, its material options, applications, and key advantages, helping you understand why it remains a go-to solution for many industries.
What is Urethane Casting?
Urethane casting process, also known as polyurethane casting, is a manufacturing process used to produce high-quality plastic parts by pouring liquid urethane into a mold, typically made of silicone. At its core, urethane casting involves the use of cast urethane materials to produce parts that mimic the properties of injection-molded plastics.
Ideal for low to medium-volume production, urethane casting process is a cost-effective alternative to more traditional methods like injection molding service. The cast urethane process allows for the creation of components with varying levels of flexibility, hardness, and durability, making it highly versatile. It’s often used in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to consumer electronics, where the demand for molded prototypes or short production runs is high.
Key Components of Urathane Casting Process
The success of urethane casting relies on two critical components:
Silicone Mold Casting: Silicone molds are created using a master pattern, which serves as the reference for the final parts. These molds are known for their flexibility, heat resistance, and ability to reproduce fine details accurately.
Liquid Urethane: The casting process uses liquid urethane, a versatile material that can be formulated to achieve specific properties, such as hardness, elasticity, or transparency. These formulations are referred to as cast urethane materials and are chosen based on the application needs.
How Urethane Casting Works?
Casting with urethane offers an efficient, adaptable, and reliable approach to producing parts with outstanding quality. This process is widely regarded as a bridge between resin casting prototypes and high-volume manufacturing, enabling designers to iterate rapidly while maintaining design integrity.
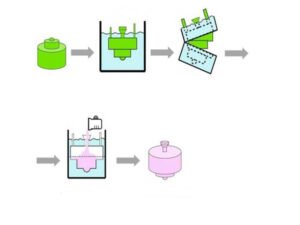
Master Pattern Creation
A master pattern, often produced through 3D printing or CNC machining, is crafted to represent the desired final part. This pattern must be precise, as it determines the accuracy of the silicone mold.
Silicone Mold Fabrication
The master pattern is encapsulated in liquid silicone, which is then cured to form a mold. Once hardened, the mold is carefully cut to remove the pattern, leaving behind a cavity that matches the original design.
Mixing and Pouring Urethane
Liquid urethane, composed of two-part resin and hardener, is mixed and degassed to remove air bubbles. This mixture is poured into the silicone mold cavity under vacuum to ensure even distribution and eliminate voids.
Curing Process
The filled mold is placed in an oven or left at room temperature to cure. Depending on the material and part complexity, curing may take a few hours to a day.
Demolding and Finishing
Once the urethane has solidified, the part is removed from the mold. Post-processing steps like trimming, painting, or adding surface textures may be applied to enhance the final appearance.
Mastering Urethane Casting Perfection | 200+ Functional Prototypes Validated
Materials Used in Urethane Casting
From rigid plastics to flexible elastomers, cast urethane materials can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements.
Types of Urethane Casting Materials
Urethane materials are generally categorized into two primary types: rigid and flexible. Each type has specific formulations designed to mimic the properties of other materials like rubber, ABS, or polycarbonate.
Rigid Polyurethane Materials: These are ideal for parts requiring structural strength and dimensional stability. Commonly used for applications such as housings, fixtures, and molded prototypes, rigid urethanes can replicate the mechanical properties of hard plastics.
Flexible Urethane Materials: These materials offer elasticity and are perfect for products like seals, gaskets, and shock-absorbing components. Flexible urethanes mimic materials like natural rubber or silicone and are often used in rubber casting.
Specialized Urethanes: Formulations with specific properties, such as transparency, high-temperature resistance, or UV stability, can also be used in polyurethane molding to meet unique application needs.
Rigid vs. Flexible Urethane Options
Rigid Urethane:
Applications: Durable enclosures, fixtures, and structural components.
Advantages: Excellent dimensional accuracy, high stiffness, and superior surface finish.
Limitations: Less suitable for dynamic applications requiring flexibility or impact absorption.

Flexible Urethane:
Applications: Seals, grommets, vibration dampers, and ergonomic grips.
Advantages: High elasticity, wear resistance, and ability to absorb impacts.
Limitations: Lower load-bearing capacity compared to rigid counterparts.

Applications of Urethane Casting
Urethane casting is a versatile process used in a wide range of applications, from rapid prototyping to low-volume production. Its ability to replicate the properties of various materials while offering speed and cost efficiency makes it an invaluable tool in diverse industries. Whether you’re validating designs, producing molded prototypes, or transitioning to mass production, urethane cast molding provides an ideal solution.
Prototyping and Design Validation
One of the primary uses of urethane casting is in prototyping, where speed and precision are essential. By using casting for prototypes, companies can create parts that closely resemble the final product in terms of material properties, appearance, and functionality. This rapid turnaround allows for quick design iterations, helping engineers identify potential issues before committing to more expensive manufacturing methods like injection molding.
Bridge Tooling from Prototyping to Mass Production
Bridge tooling refers to using urethane casting as an intermediate solution when transitioning from prototype to full-scale production. This application is particularly beneficial when there’s a need to quickly produce parts in moderate quantities before committing to expensive, high-volume tooling for injection molding. Urethane molds can be used to produce parts with near-identical properties to those made with injection molds, allowing companies to meet customer demands while maintaining the flexibility to refine the product.
Low-Volume Production
In industries where high-volume production isn’t necessary or feasible, urethane casting is an excellent choice for low-volume production. This process allows businesses to produce parts efficiently without the need for the expensive molds required for injection molding. Whether it’s for custom orders, limited-edition products, or testing smaller markets, urethane casting provides flexibility and cost savings.
Urethane Casting vs. Injection Molding
Understanding the key differences between the two processes can help manufacturers determine which method best aligns with their project needs, budget, and timeline.
Differences in Tooling Costs and Setup
Urethane Casting: The tooling required for urethane casting is far less expensive than that for injection molding. Urethane molds are made from silicone, which is flexible, easy to work with, and can be created quickly.
Injection Molding: In contrast, injection molding requires the creation of a steel or aluminum mold, which is both time-consuming and expensive. The mold must be meticulously designed, often requiring advanced CAD modeling and detailed specifications to ensure accuracy. As a result, the initial tooling costs for injection molding can be prohibitively high.

Suitability for Different Production Volumes
Urethane Casting: Urethane casting is highly suited for low-volume production, typically ranging from a few parts to several hundred. Because of the low cost of molds, manufacturers can easily create small batches of custom parts.
Injection Molding: Injection molding, on the other hand, is designed for high-volume production, with thousands or even millions of parts being produced from the same mold.
Material Options and Performance Characteristics
Urethane Casting: Cast urethane materials offer a wide range of options in terms of rigidity, flexibility, and hardness. These materials can replicate the look and feel of various plastics, rubbers, and even metals. With the ability to adjust the chemical composition, manufacturers can produce materials with specific properties such as abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, or high thermal stability.
Injection Molding: Injection molding uses primarily thermoplastics, which can be rigid or flexible depending on the material used, including options like ABS, polyethylene, polypropylene, and specialized engineering plastics like polycarbonate or nylon.
When to Choose Urethane Casting?
Urethane casting stands out as a preferred manufacturing solution in many scenarios where speed, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness are key.
In industries where rapid casting and short timelines are critical, urethane casting offers a powerful alternative. It provides the flexibility to produce parts that are virtually indistinguishable from those made using traditional injection molding, but with a much quicker turnaround. Whether you’re testing a new product design or looking to produce small runs of custom parts, urethane casting delivers both speed and precision.
Conclusion
Urethane casting process stands as an indispensable solution for many industries, offering numerous advantages that make it the preferred choice for prototyping and low-volume production. It offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional methods like injection molding, especially in scenarios where low-volume production or customized parts are required. If you’re considering a casting process for your next project, China Jiangzhi professional manufacturer will supply urethane casting services.



