EPDM rubber is a highly versatile and durable material, prized for its ability to withstand extreme weather conditions, UV rays, ozone, and high temperatures. This article explores the key properties and advantages of EPDM rubber, highlighting its widespread use across various industries, from automotive to construction. While it excels in durability and environmental resistance, it also has some limitations that need to be considered. Discover how EPDM rubber molding can provide long-lasting solutions and why it continues to be a preferred choice for critical applications.

What is EPDM Rubber?
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer rubber, commonly known as EPDM rubber, is a highly durable synthetic rubber widely used across various industries. This elastomer is composed of ethylene, propylene, and a diene monomer, which enhances its cross-linking capabilities, making it exceptionally resistant to environmental degradation. EPDM material is particularly valued for its outstanding resistance to extreme weather conditions, ozone exposure, and moisture, making it an essential choice for industrial, automotive, and construction applications.
Due to its ability to withstand harsh environments, EPDM elastomer has become a staple in the production of rubber seals, EPDM gaskets, and EPDM composite materials used in diverse sectors. Whether in EPDM for buildings, automotive components, or industrial machinery, this synthetic rubber delivers unparalleled performance in demanding conditions.
Key Properties of EPDM Rubber
Weather and UV Resistance
One of the most defining characteristics of EPDM material is its exceptional resistance to weathering and ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Unlike many other rubbers that degrade when exposed to prolonged sunlight, EPDM elastomer remains intact and retains its flexibility over extended periods.
This property makes EPDM construction materials a preferred choice for roofing membranes, window seals, and outdoor gaskets. In applications where prolonged exposure to the elements is inevitable, EPDM in industry ensures longevity and consistent performance, preventing premature cracking and deterioration.
Heat and Cold Tolerance
Extreme temperature fluctuations can cause some materials to harden, crack, or lose their elasticity. However, EPDM rubber advantages include its high temperature resistance, allowing it to perform efficiently across a broad temperature range.
Capable of withstanding temperatures from -50°C to over 150°C, EPDM elastomer is ideal for environments that experience significant thermal variations. This quality is particularly useful in EPDM gaskets and rubber seals for automotive cooling systems, industrial steam applications, and HVAC ducting, where temperature extremes are commonplace.
Chemical and Ozone Resistance
Unlike natural rubber, which is susceptible to chemical degradation, EPDM material exhibits strong resistance to a wide array of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents. Additionally, its excellent ozone resistance prevents cracking and deterioration caused by atmospheric oxidation.
These properties make EPDM composite materials a reliable choice for harsh industrial settings where exposure to aggressive chemicals is a concern. Whether in factory environments, chemical plants, or automotive fluid systems, EPDM elastomer ensures stability and longevity.
Water and Steam Resistance
Water infiltration and steam exposure can lead to the breakdown of many rubber materials over time. However, EPDM rubber excels in these conditions, maintaining its integrity even under continuous exposure to moisture and pressurized steam.
This quality is essential in applications such as EPDM for buildings, roofing membranes, and EPDM construction materials, where prolonged contact with rain, humidity, and steam could otherwise compromise performance. Additionally, EPDM rubber suppliers recommend this material for plumbing seals and industrial-grade waterproofing solutions.
Durability and Longevity
Perhaps one of the most critical EPDM rubber advantages is its impressive lifespan. Unlike many other synthetic rubbers, EPDM elastomer resists wear and tear, ensuring long-term performance with minimal maintenance.
With a service life that can exceed 50 years in optimal conditions, EPDM material is a cost-effective investment for industries requiring durable sealing, insulation, and protective solutions. Whether used in automotive applications, EPDM gaskets, or large-scale infrastructure projects, its resilience makes it a go-to choice for engineers and manufacturers worldwide.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Weather and UV Resistance | Resistant to prolonged sunlight exposure, prevents cracking and degradation, ideal for outdoor applications. |
| High Temperature Resistance | Withstands temperatures ranging from -50°C to over 150°C, making it suitable for extreme heat and cold environments. |
| Chemical and Ozone Resistance | Resists oxidation, ozone, acids, alkalis, and many industrial chemicals, ensuring longevity in harsh conditions. |
| Water and Steam Resistance | Maintains flexibility and integrity when exposed to moisture, humidity, and pressurized steam, ideal for roofing and plumbing applications. |
| Durability and Longevity | Has a lifespan of over 50 years under optimal conditions, making it a cost-effective and low-maintenance material. |
| Flexibility and Elasticity | Retains elasticity even at low temperatures, ensuring reliable sealing and insulation performance. |
| Electrical Insulation | Provides excellent dielectric properties, making it suitable for electrical and cable insulation applications. |
| Environmental Sustainability | Recyclable and energy-efficient, contributes to sustainable construction and manufacturing practices. |
Advantages of Using EPDM Rubber
Weather and UV Resistance
EPDM rubber is highly resistant to UV rays, ozone, and extreme weather conditions, making it ideal for outdoor applications like EPDM gaskets and rubber seals.
High Temperature Resistance
It can withstand temperatures from -50°C to over 150°C, making it perfect for automotive and industrial applications exposed to extreme heat.
Chemical and Ozone Resistance
EPDM resists many chemicals, acids, alkalis, and ozone, preventing cracks in harsh environments like chemical plants and fuel systems.
Water and Steam Resistance
It’s highly resistant to water and steam, making it ideal for roofing, plumbing, and EPDM construction materials.
Low Maintenance and Long Lifespan
EPDM lasts over 50 years, reducing the need for frequent replacements and making it cost-effective.
Environmentally Friendly
EPDM is recyclable and energy-efficient to produce, making it a sustainable choice for industries focusing on environmental responsibility.
Disadvantages of Using EPDM Rubber
Limited Oil and Hydrocarbon Resistance
EPDM deteriorates quickly when exposed to oils and hydrocarbons, making it unsuitable for fuel systems.
Adhesion Issues
It can be challenging to bond EPDM to certain metals and plastics, requiring special adhesives or primers.
Higher Initial Cost
EPDM can be more expensive upfront compared to other rubbers, although its longevity makes it cost-effective in the long run.
Swelling in Some Chemicals
EPDM may swell when exposed to polar solvents like ketones and alcohols, limiting its use in certain chemical environments.
Not Ideal for High-Friction Applications
EPDM lacks the abrasion resistance needed for high-friction environments, making it unsuitable for dynamic seals or conveyor belts.
EPDM Molding Solutions
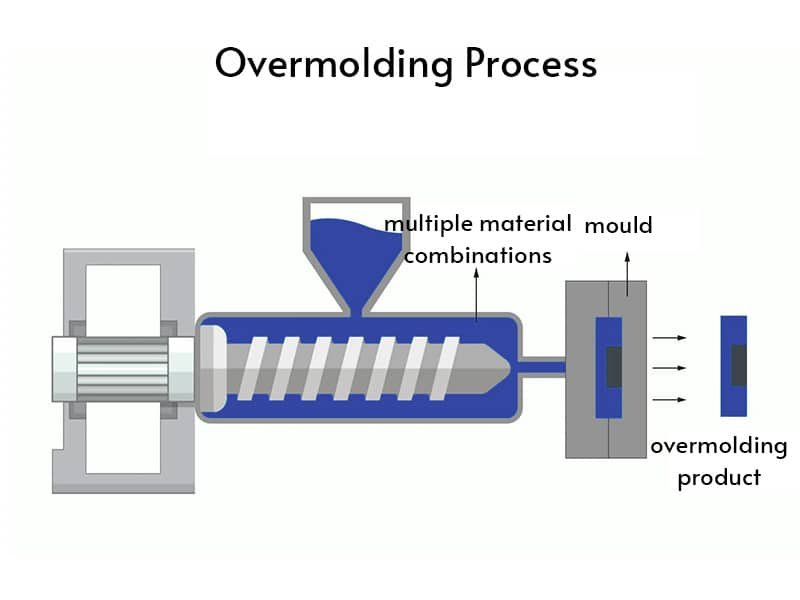
While EPDM rubber is widely used in various industries, its effectiveness is significantly influenced by the manufacturing process. EPDM molding methods, such as injection molding and compression molding, play a crucial role in shaping the final product.
Injection Molding for EPDM Rubber
Injection molding is a highly efficient manufacturing process for producing EPDM rubber components with precise dimensions and complex geometries. This method involves injecting heated EPDM material into a mold cavity under high pressure, ensuring excellent consistency and repeatability.
Advantages of EPDM Injection Molding:
- Ideal for high-volume production
- Produces intricate and detailed parts
- Ensures uniformity and minimal material waste
- Provides excellent mechanical properties
Compression Molding for EPDM Rubber
Compression molding is another common method used for shaping EPDM rubber, especially for larger or thicker components. In this process, pre-measured EPDM material is placed into a heated mold, where it is compressed under pressure to form the desired shape.
Advantages of EPDM Compression Molding:
- Suitable for low to medium production volumes
- Cost-effective for larger parts
- Allows for a wide range of material formulations
- Provides strong, durable rubber components
By utilizing advanced EPDM molding solutions, manufacturers can enhance the performance and durability of rubber components, ensuring they meet the rigorous standards of various industries.
Common Applications of EPDM Rubber Molding
Automotive Industry
EPDM elastomer is commonly used in rubber seals, EPDM gaskets, and hoses in vehicles, ensuring long-lasting performance even under extreme conditions.
- Weatherstripping and Seals
- Coolant and Radiator Hoses
- Brake System Components
- Windshield Wiper Blades
Construction and Roofing
The material’s outstanding resistance to UV radiation, ozone, and moisture makes it a go-to option for architects and contractors.
- EPDM Roofing Membranes
- Sealing and Waterproofing
- Pipe and Duct Insulation
Electrical Insulation
EPDM’s excellent dielectric properties make it an ideal synthetic rubber for electrical insulation applications.
- Cable and Wire Insulation
- Transformer and Power Distribution Components
- Protective Covers and Gaskets
Industrial and Manufacturing Uses
- EPDM Gaskets and Seals
- EPDM Vibration Dampening
- EPDM Steam and Chemical Hoses
Consumer Goods
EPDM elastomer is also used in everyday consumer products, enhancing their performance and longevity.
- Appliance Seals and Tubing
- Sports and Playground Surfaces
- Garden Hoses and Water Seals
Conclusion
EPDM rubber is highly durable and resistant to weather, UV rays, ozone, extreme temperatures, and water, making it ideal for industries like automotive, construction, and manufacturing. Its long lifespan, low maintenance, and eco-friendly properties further enhance its value. However, it has limitations, such as poor resistance to oils and hydrocarbons, challenges with adhesion, and higher initial costs. Despite these drawbacks, EPDM’s advantages, like its excellent chemical resilience and flexibility, make it a reliable and cost-effective choice for applications like gaskets, roofing, and seals.
By incorporating EPDM molding solutions, such as injection and compression molding, manufacturers can maximize the material’s benefits while ensuring the production of high-quality, durable rubber components tailored to specific industrial needs.