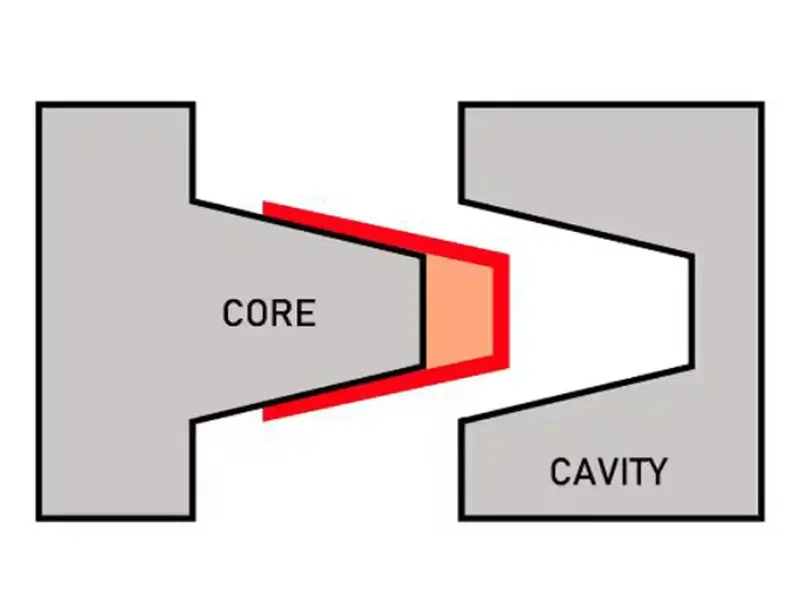
Injection Molding Design Guide
Quick Injection Molding Design Hot Topics
- Wall Thickness
- Draft Angle
- Corner Design
- Ribs and Gussets
- Boss Design
- Threading
- Snap Fit
- Holes
- Living Hinge
- Undercuts
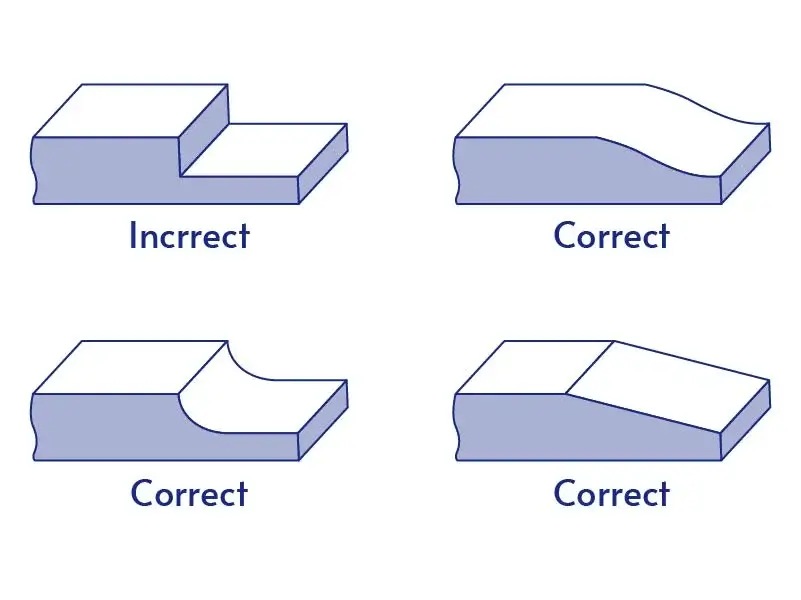
Wall Thickness
- Minimize Thickness: Reduce cost savings without losing strength.
- Flow & Cooling: Adjust thickness for better material flow and efficient cooling.
- Reinforcement: Strengthen thin-wall areas.
- Consistency: Avoid thick variations to ensure uniform cooling and parting lines.
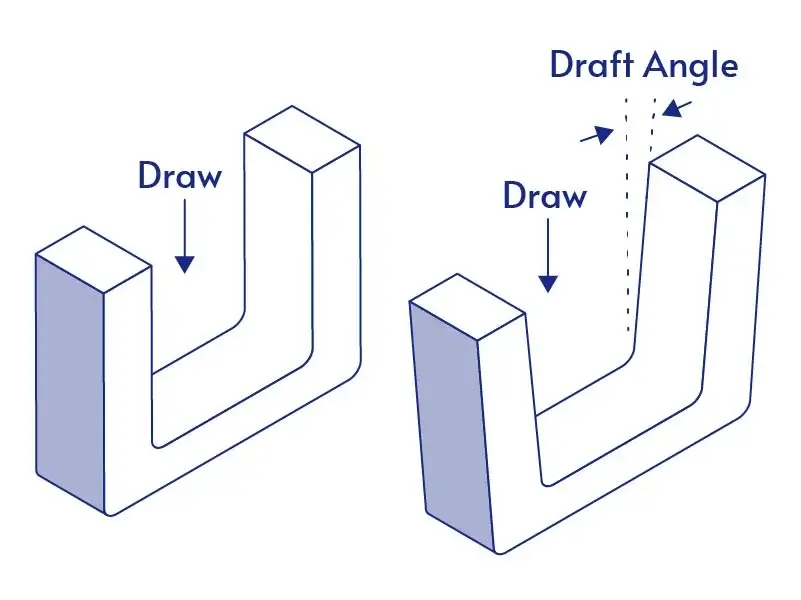
Draft Angles
- Smooth Demoulding: Ensures easy release without damage.
- Optimal Angle: 1°-3°— too small causes sticking, too large affects appearance.
- Shape: Complex parts may need a larger angle.
- Material: Adjust angles for better results.
- Mold Life: reduces mold wear and extends mold life
- Surface Quality: Excessive draft impacts parting line and finish.
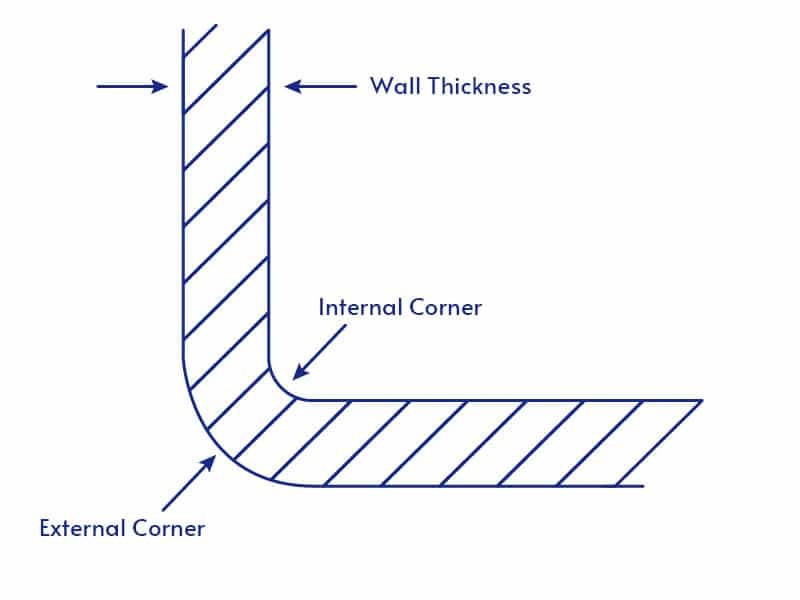
Corners Design Guide
- Round Corners: Avoid sharp angles to reduce stress and improve durability. Interior Angles: Larger radii prevent incomplete filling and uneven cooling.
- Outer Corners: Ensure smooth flow to avoid stress.
- Transition Angles: Smooth transitions reduce stress and mold wear.
- Wall Thickness: Coordinate with corner design for even flow and cooling.
- Reinforcement: Proper reinforcement maintains corner strength without disrupting flow.
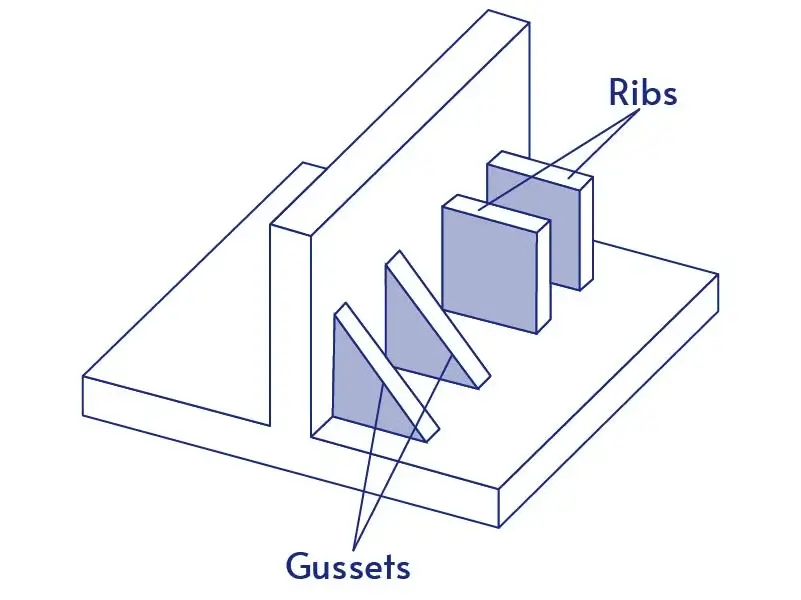
Ribs and Gussets
- Stress Distribution: Ensure even stress distribution to avoid fatigue or deformation.
- Cooling & Flow: Well-designed ribs improve cooling and material flow, reducing defects.
- Die Life: Avoid complex rib designs to prevent mold wear and extend lifespan.
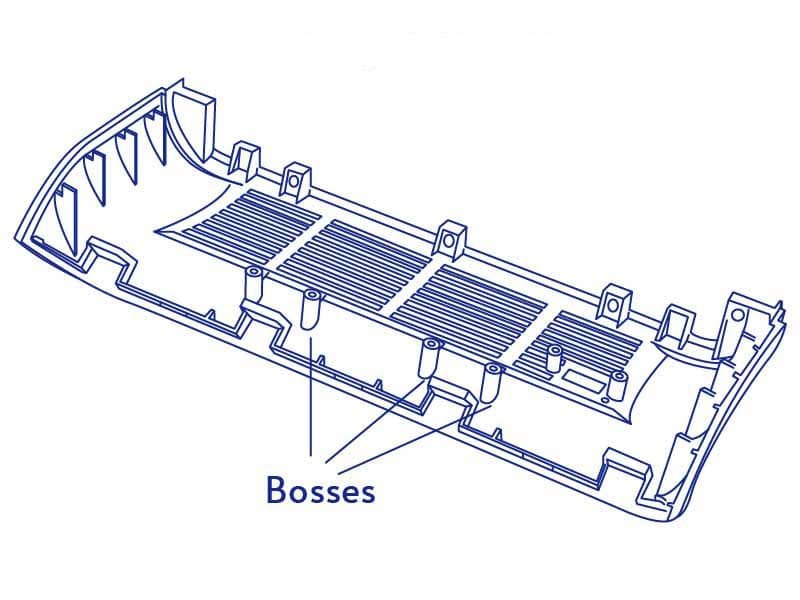
Boss Design Guide
- Size: Boss diameter 1.5-2x wall thickness for strength.
- Height: Limit to 3x wall thickness.
- Thickness: Thicker walls for strength and even cooling.
- Transitions: Smooth transitions reduce stress.
- Reinforcement: Add where extra strength is needed.

Injection Molding Thread
- Thread Type: Choose from external, internal, or blind threads based on the product’s needs.
- Thread Size: Follow standard sizes to maintain connection strength and avoid molding difficulties.
- Thread Depth: Keep thread depth no greater than 1.5 times the wall thickness to ensure smooth material flow.
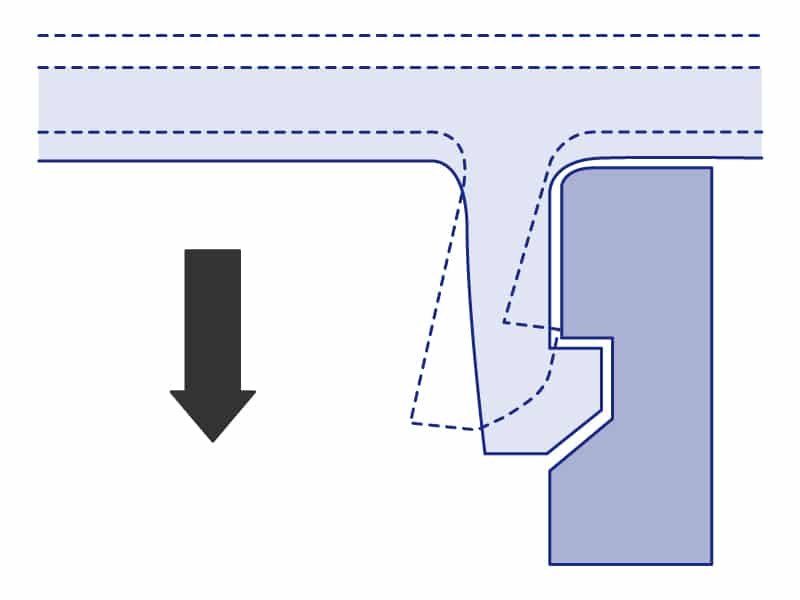
Snap Fit Design Guide
- Material: Choose elastic materials to prevent fatigue.
- Buckle Shape: Ensure stability and resistance to external forces.
- Hook Position: Provide enough contact area for a secure fit.
- Demolding Angle: Use a 1°-3° angle for a smooth release.

Holes in Injection Molding
- Hole Size: Choose hole size carefully to avoid molding defects like incomplete filling
- Position: Avoid placing holes at parting surfaces to prevent stripping issues.
- Reinforcement: Reinforce around holes to maintain strength.
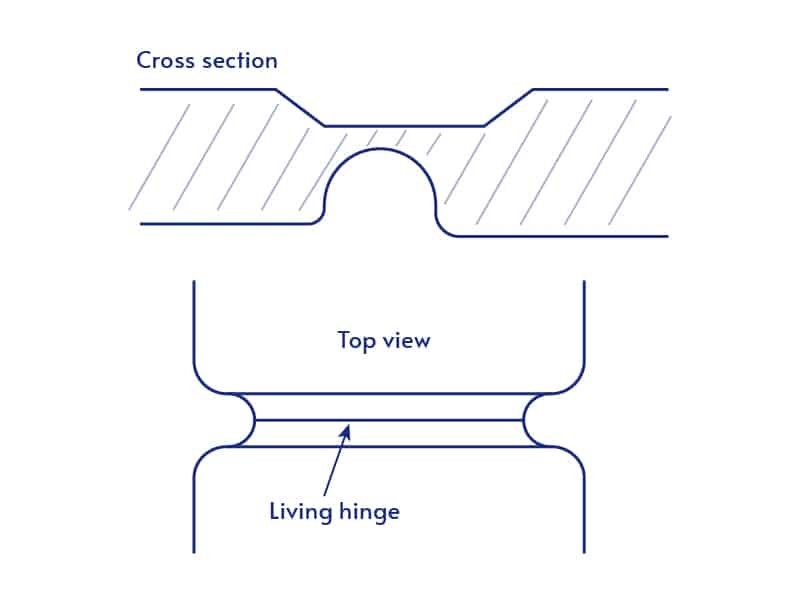
Living Hinge Design
- Material Selection: Use flexible, fatigue-resistant thermoplastics like polypropylene.
- Hinge Thickness: Maintain a thickness between 0.3mm and 1.5mm for flexibility.
- Bending Radius: Avoid sharp bends and ensure a large enough radius to reduce stress and prolong hinge life.
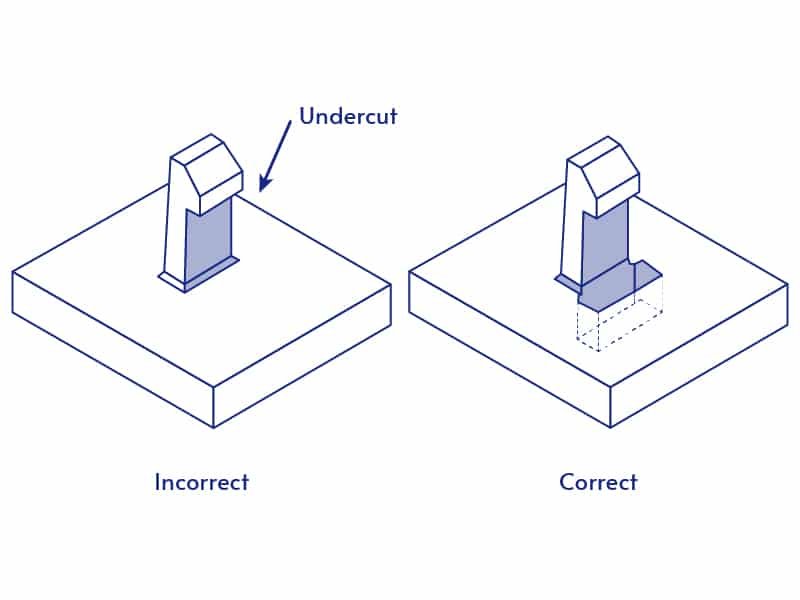
Undercuts Design Guide
- Demolding Difficulty: Undercuts require special mold structures such as sliders or core pulls, raising costs.
- Die Complexity: Under-cuts increase mold complexity, leading to higher maintenance costs.
- Stress Concentration: Undercuts can cause stress concentration, increasing the risk of cracking.
- Material Flow: Complex concave shapes may cause incomplete filling and uneven cooling.
Professional Injection Molding One-Stop Service Company
FAQs About Injection Molding Design Guide
Pick a material based on strength, temperature resistance, and cost. PP and PE are flexible and budget-friendly, while ABS and PC offer better strength and heat resistance. Need help to choose? Let’s talk about your project!
Or you can read our ultimate guide on injection molding material selection.
To ensure a smooth project, we recommend that you provide the following information:
- 2D/3D drawings or design sketches.
- Target material and performance requirements (e.g. strength, heat resistance).
- Annual production estimates and budget ranges.
Based on this information, our engineers will provide you with professional advice and help you improve your design.
The project cycle is divided into the following stages:
- Design stage: 2 weeks for simple products, 4-6 weeks for complex products, including DFM (Manufacturability analysis).
- Mold production: standard mold 6-8 weeks, high-precision or multi-cavity mold 8-12 weeks.
- Production stage: After the mold is completed, the sample can be delivered within 3 days, mass production depends on the order quantity.
Our transparent project management platform provides real-time updates to ensure your project is completed on time.
For complex functional design, we recommend:
- Living Hinge: integrated flexible connection to reduce assembly costs.
- Insert molding: Metal or electronic components are embedded directly in plastic.
- Multi-color or multi-material molding: achieve visual and functional diversification.
Curious about how these solutions could work for your project? Let’s brainstorm together!
Sure! We can personalize your product by achieving specific patterns or textures through die etching, laser engraving or secondary processing such as heat transfer, spray painting.
Share your ideas, and Jiangzhi will help you turn them into production-ready designs that are as innovative as they are practical.
Learn our custom services on surface finishing.
Absolutely! For example:
- Sensor embedding: Intelligent function.
- Surface coating treatment: Added anti-corrosion, anti-scratch or anti-bacterial properties.
- Multi-component integration: multiple parts are integrated through secondary injection molding.
Want to know more application scenarios? Contact Jiangzhi to discover your unique solution!
Of course! We provide a "one-stop service" from product design, rapid prototyping, mold development to mass production, so that your product quickly from concept to reality. Even if it is a vague idea at the beginning, we can help you clarify it until it is mass-produced.