Custom Insert Molding Service
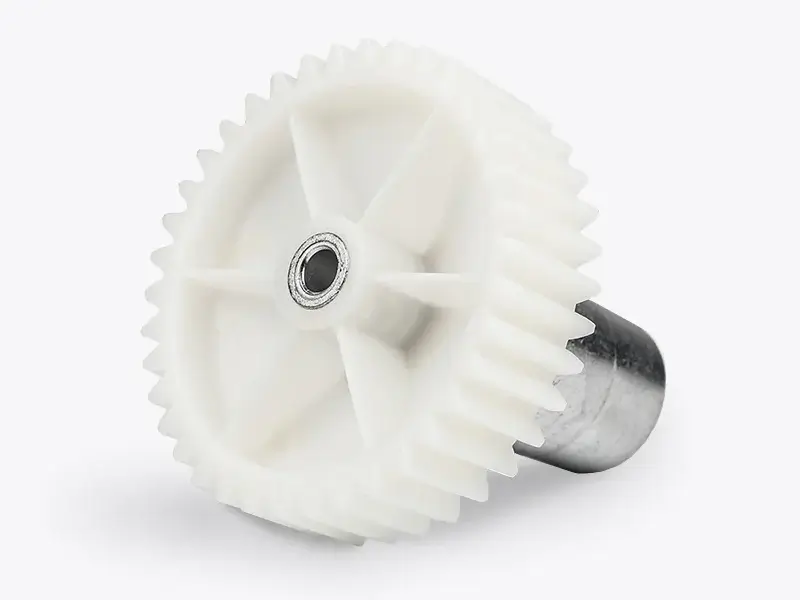


We know how frustrating it can be when assembly is complicated, parts don’t hold up, or production slows you down. That’s where our insert molding solutions shine. By combining metal, ceramic, or other inserts with plastic in a single step, we boost bond strength by up to 50% and reduce your process steps by about 30%. This means fewer steps, stronger parts, less waste, and faster time to market.
What Is Insert Molding Service?
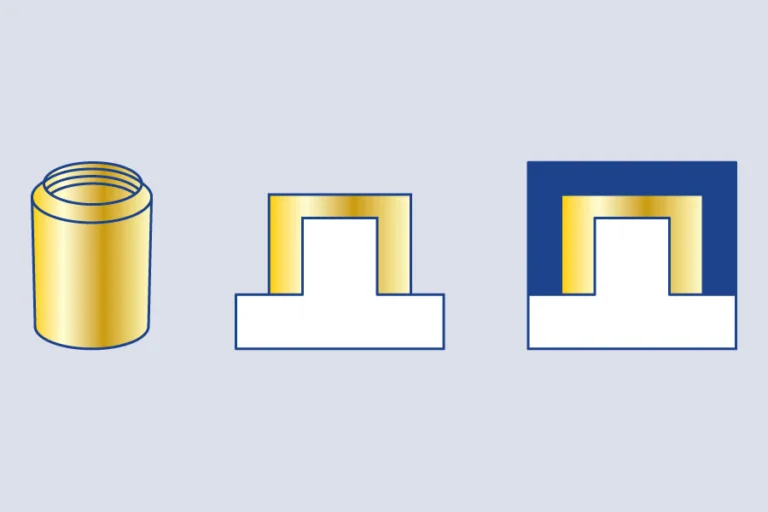
Insert molding is an advanced injection molding process that combines metal, plastic, or ceramic components into a single, integrated part. By placing pre-formed inserts into a mold and overmolding them with plastic, insert molding creates strong, multifunctional components while eliminating the need for secondary assembly or adhesives. This not only enhances structural integrity but also streamlines production and improves overall product performance.
At Jiangzhi, we specialize in custom insert molding services tailored to your exact requirements. Work with us to optimize your design, shorten your production timeline, and achieve greater product value, all backed by decades of manufacturing experience and a commitment to quality.
Insert Molding Services Material
Inserts Molding Materials
The material surrounding the inserts, or the overmold, is selected based on design and performance requirements. It can be made from plastics, rubbers, or TPU to securely encapsulate the inserts.
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyamides/Nylon (PA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polyurethane (PU)
- Natural Rubber (NR)
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Insert Types
Inserts for insert molding are typically made from metal, plastic, ceramic, or other durable materials, and many types of components, from standard hardware to custom parts, can be used as inserts to meet specific design and functional needs.
- Custom insert for special need
- Screws and threaded fastener
- Electronics component
- Bearing and bushing
- Magnet
- Clip, pin, spring, and rivets
Injection Molding Material Selection Guide
How Does Insert Injection Moulding Process Work?
Insert Preparation
Insert Placement
Mold Clamping
Plastic Injection
Cooling & Solidification
Cooling and Ejection
Customized Insert Molding Products
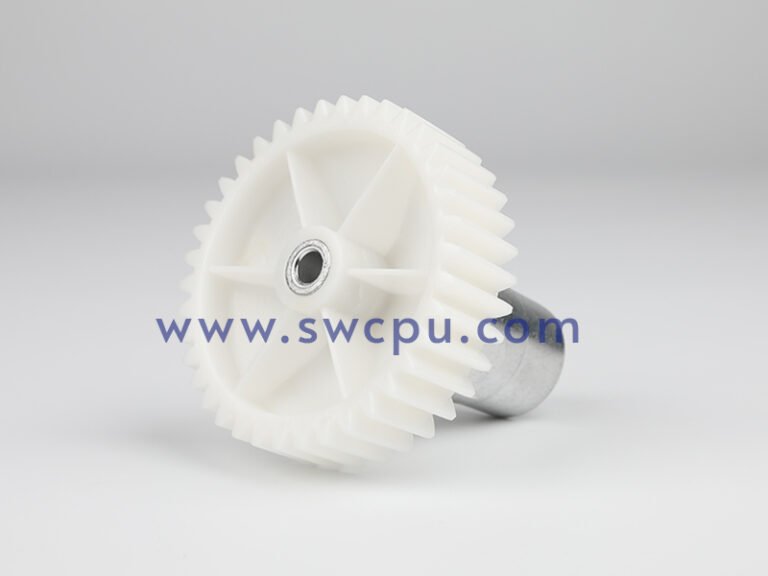
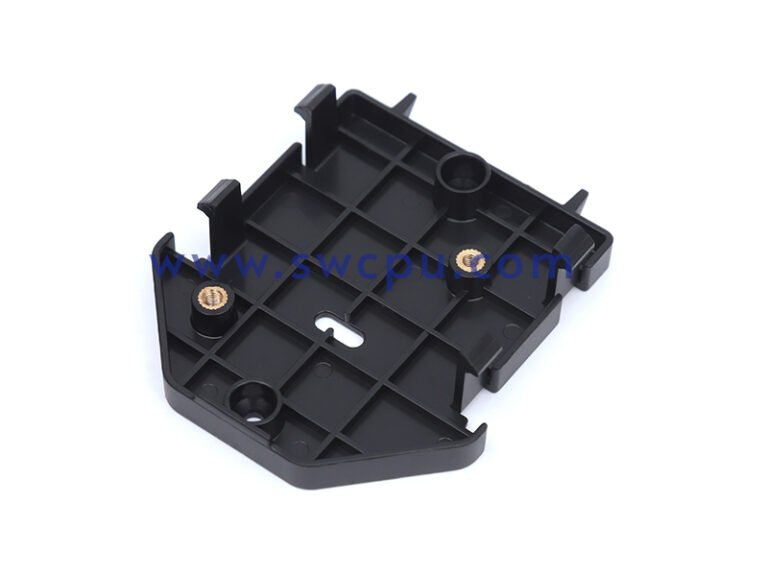
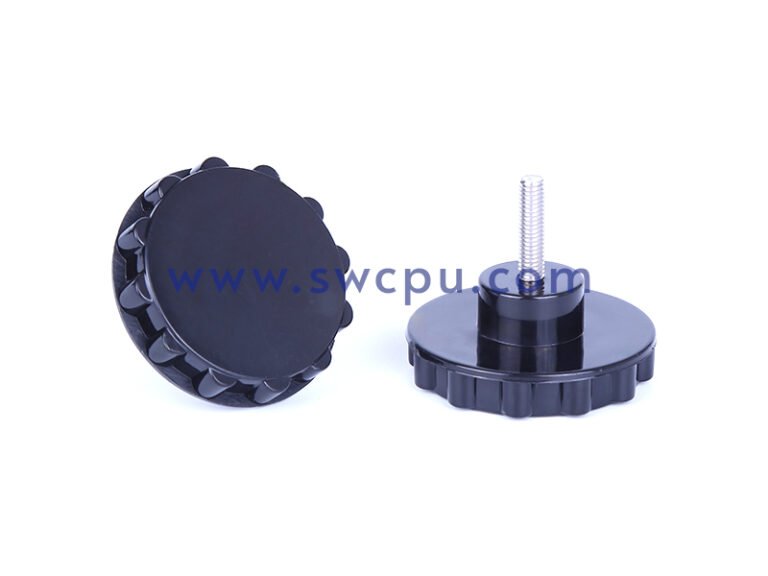
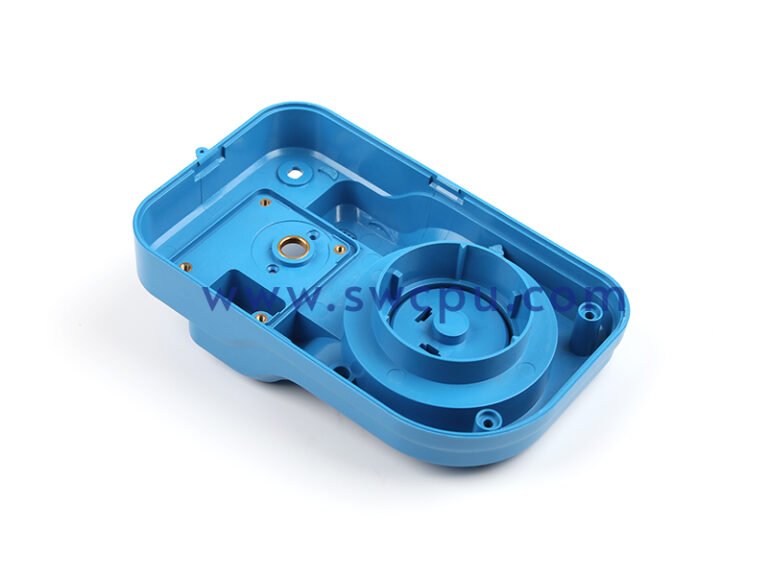
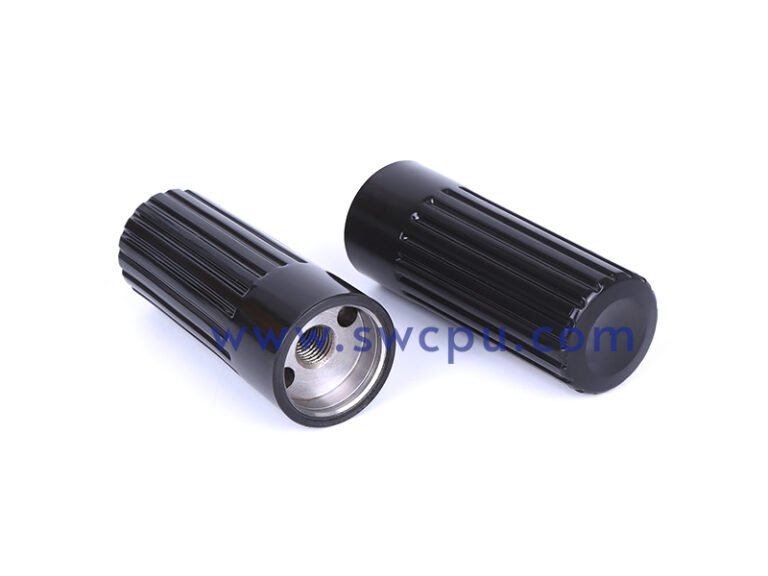
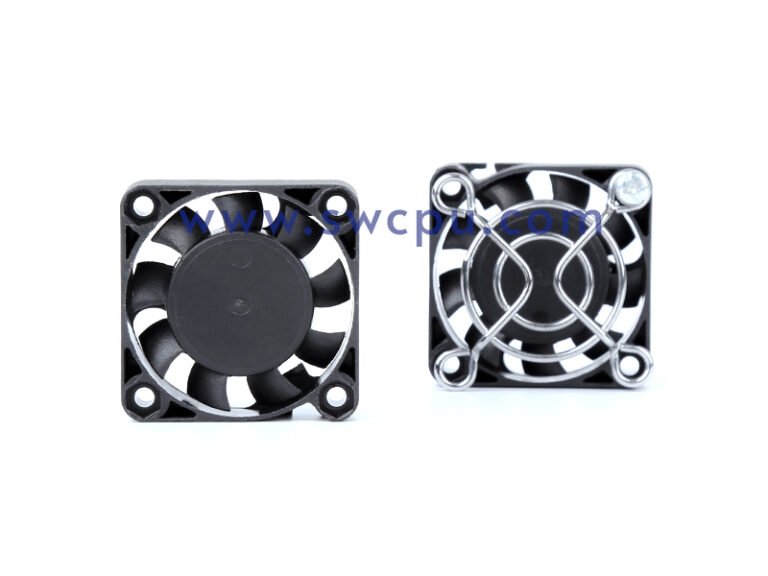
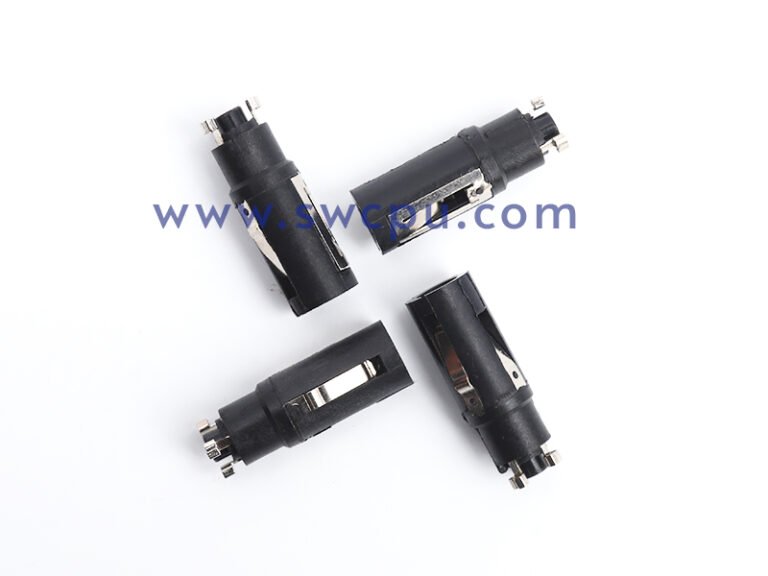
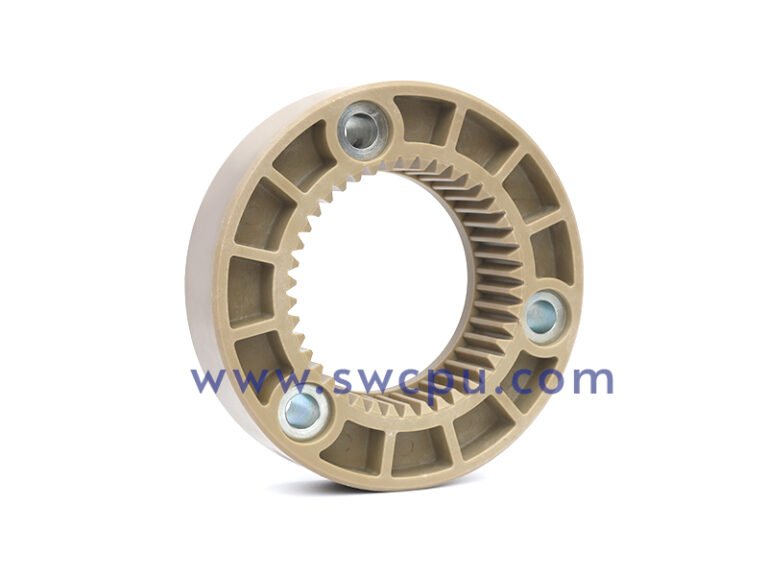
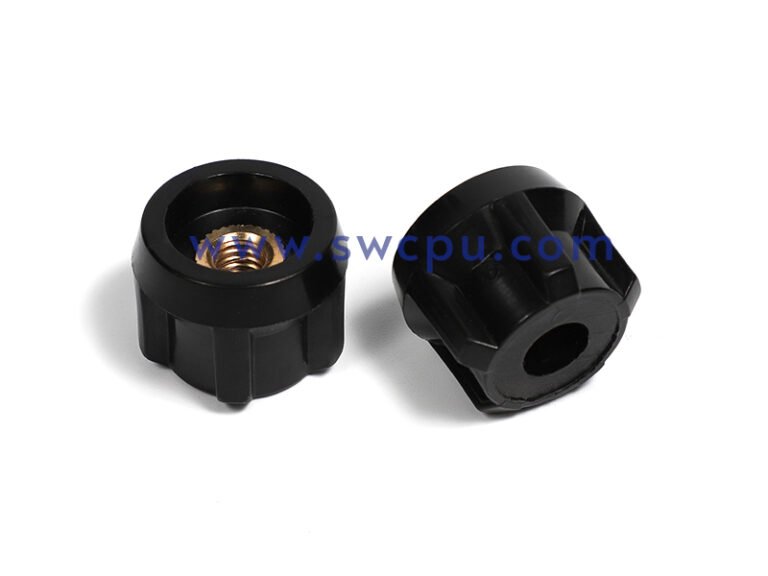
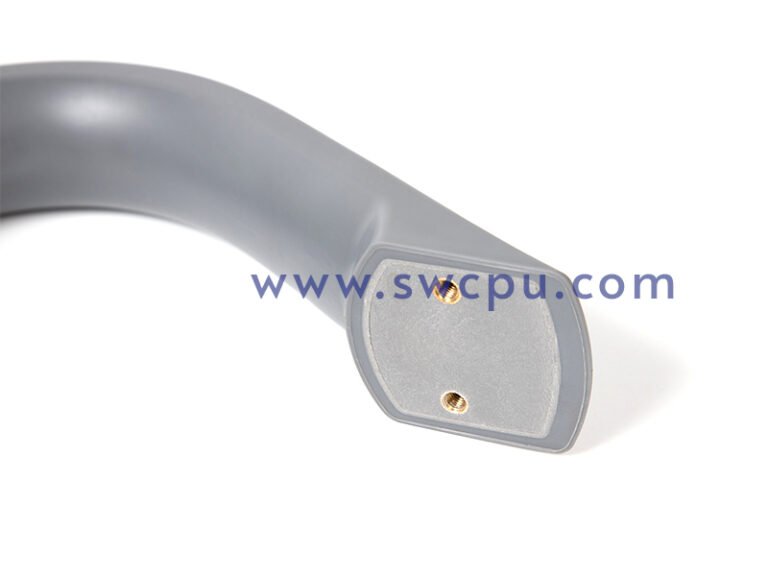










Custom Contract Manufacturing Capability
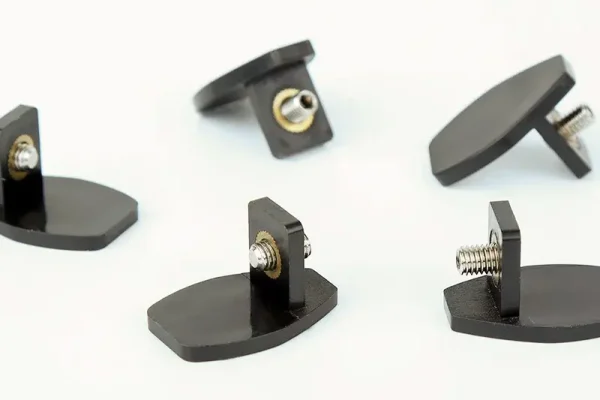
Advantages of Insert Molding Process
- Combines multiple functions in one part
- Eliminates need for secondary assembly steps
- Enhances part durability, strength, and appearance
- Compatible with various insert types and shapes
- Reduces overall manufacturing cost

Application of Insert Molding Service
- Electrical Connector
- Auto Instrument panel group
- Car Seat Parts
- Medical Catheters and Fittings
- Insert Molded Housings
- Computer Accessories
- Fasteners and threaded parts
Metal & Plastic Insert Molding Components Application
Insert molding is widely used across industries to create strong, precise, and reliable components. It allows metal, electrical, or structural inserts to be integrated directly into plastic parts, making it ideal for applications that need durable, high-performance insert components with minimal assembly.
Why Choose Us Insert Moulding Service?
High Precision & Consistent Quality
Fast Turnaround & Flexible Capacity
Expert Engineering Support
One-Stop Prototyping & Small-Batch Solution
One-Stop Insert Molding Solution Manufacturer
From prototyping to full-scale production, we deliver custom plastic and rubber parts with accuracy, efficiency, and minimal waste.
Jiangzhi Other Processing Services
FAQs of Insert Molding
How does plastic insert molding improve productivity?
By integrating inserts with plastic parts, insertion molding eliminates assembly steps and improves production efficiency, especially for mass production.
What inserts can I use for custom insert molding service?
Inserts can be metal (such as steel, aluminum, copper), ceramic, or hard plastics, depending on the strength, corrosion resistance, and other requirements of the final product. Don’t know how to choose, let the Jiangzhi help you!
How long is the production cycle of insert molding?
The production cycle of custom insert molding depends on several factors, such as mold complexity, part size, and production volume. Generally speaking, The single production cycle of insert molding is usually between 1 and 5 minutes, but this also needs to be adjusted according to the specific production conditions. In mass production, the cycle may be shorter, because the mold and equipment have entered a stable working state.
Does the insert move during insert moulding?
Is the insertion firmly attached to the plastic? Is there a risk of falling off?
In the Insert Molding process, the attachment of the insert to the plastic is usually very strong. By precisely controlling the mold temperature, injection pressure and cooling rate, we are able to ensure a strong bond between the insert and the plastic. To ensure the highest quality, we carry out rigorous quality testing on each product, including strength testing, adhesion testing and dimensional accuracy checks to eliminate the risk of falling off.
What are the similarities and differences between overmoulding and insert moulding?
Overmoulding involves injecting a material over an existing part to add a new layer, while insert moulding embeds a pre-made component, like metal, into a plastic part. Both processes combine materials to enhance functionality, but overmoulding adds a soft or protective layer, and insert moulding integrates parts for added strength or features. Learn more about insert and overmolding details.