CNC Turning Service

What is CNC Turning
CNC Milling Capabilities
Maximum Capabilities for CNC Turning
| Part size limitations | Metric units | Imperial units |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum part diameter | 431mm | 17in |
| Maximum part length | 990mm | 39in |
| Maximum swing over the carriage | 350mm | 13.7in |
| Maximum spindle through-hole | 40mm | 1.5in |
CNC Turning General Tolerances
| Description | General Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Distance Dimensions | For features of size (Length, width, height, diameter) and location (position, concentricity, symmetry) +/- 0.1mm. |
| Orientation and Form Dimensions | ±0.1~2mm depend on part size, Angularity 1/2 degree. |
| Edge Condition | Sharp edges will be broken and deburred by default. Critical edges that must be left sharp should be noted and specified on a print. |
How CNC Milling Works
The components of a CNC lathe include: workpiece, sleeve, spindle, cutting tool and tool holder, live machining, and tool tower.
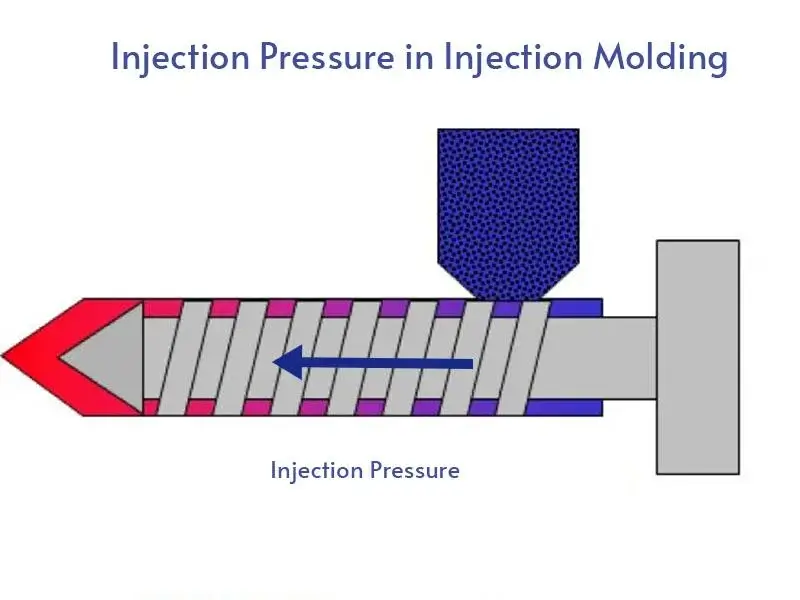
During the CNC turning process, a metal rod is rotated while a cutting tool is held against the stock to remove material and create final parts. The lathe rapidly machines your parts in a subtractive turning process with additional live tooling. Outside diameter (OD) and inside diameter (ID) threading is also available.
Turned parts can then be left as-machined, with visible tool marks, or bead blasted. When the run is complete, parts are inspected, boxed and shipped shortly thereafter.
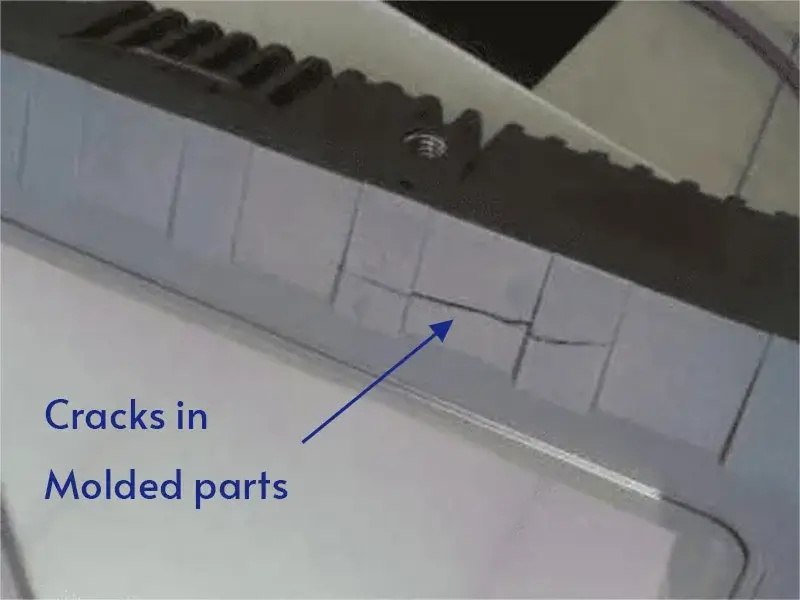
Understanding and Preventing Cracks in Molded Parts
Why Choose Us
Ensuring accurate and intricate part production
Meeting diverse industry needs
Proven track record in successful projects
Rigorous quality checks for reliable results
Contract Manufacturing Solution

Mold & Tooling Service
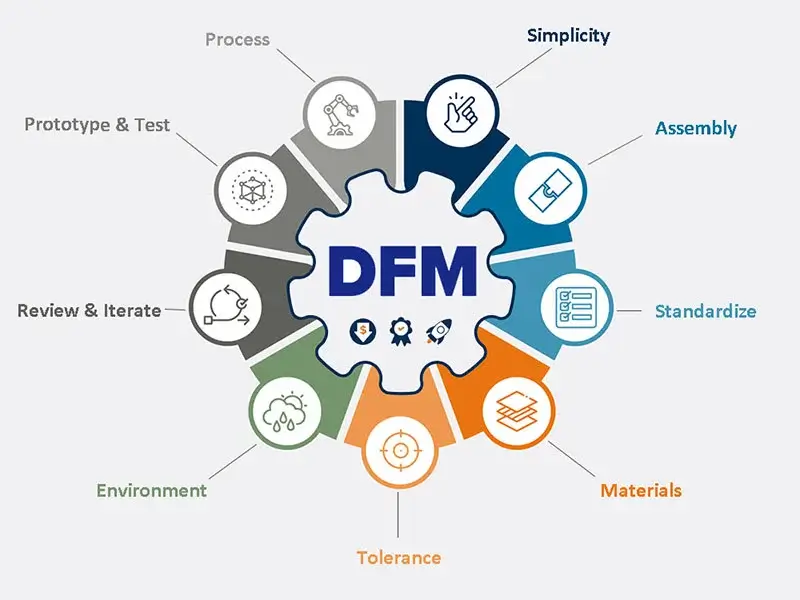
Design for Manufacturability

Surface Finishing

Assembly Manufacturing
FAQs of CNC Milling
What are the limitations of CNC turning?
CNC turning has some limitations like design restrictions. CNC turning is ideal for creating rotational, symmetric parts. But other methods such as CNC milling might be more appropriate for non-cylindrical parts.
What is the basic principle of CNC turning process?
As the piece rotates, a cutting tool is fed to the piece, which works at the material, cutting away to create the desired shape. Unlike other cutting sytles where the cutting tools themselves move and spin, in this case, the workpiece is rotated during the cutting process.
What materials are used in CNC turning?
The most common CNC turning materials include: aluminium, stainless steel, copper, brass, steel alloy, and various plastics.
How many types of CNC turning are there?
There are two broad categories of CNC turning centers, which include horizontal turning centers and vertical turning centers. Horizontal turning centers are far more common than their vertical counterparts.