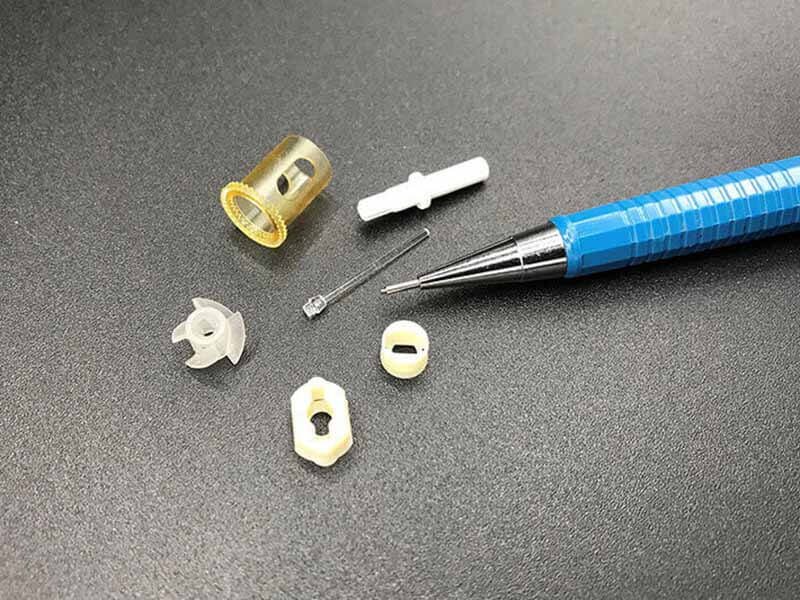
Custom Compression Molding Services

Compression Molding Capabilities
| Name | Detail |
|---|---|
| Size |
98.42in. x 78.74in. x 39.37in. 2500mm x 2000mm x 1000mm |
| Mold Cavities | Single or multi-cavity |
| Mold Life | Unlimited (We will open a new mold if the old one worn out) |
| Mold Storage | Forever |
| Mold Material | P20 Steel |
| General Tolerance | Normally +/- 0.008in.(0.2mm) |
Compression Molding Materials
Rubber Materials
- Silicone
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
- Nitrile (NBR)
- Neoprene (CR)
- SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber)
- Natural Rubber (NR)
- Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Plastic Materials
- Nylon
- PP
- HDPE
- UHMWPE

Compression Molding Surface Finishing
| Finish | Description |
|---|---|
| SPI A1 | 6000 grit diamond, surper high glossy finish |
| SPI A2 | 3000 grit diamond, high glossy finish |
| SPI A3 | 1200 grit diamond, normal glossy finish |
| SPI B1 | 600 grit paper, fine semi-glossy finish |
| SPI B2 | 400 grit paper, normal semi-glossy finish |
| SPI B3 | 320 grit paper, normal semi- |
| SPI C1 | 600 grit stone, fine matte finish |
| SPI C2 | 400 grit stone, medium matte finish |
| SPI C3 | 320 grit stone, normal matte finish |
| SPI D1 | Dry blast glass bead, satin textured finish |
| SPI D2 | Dry blast, dull textured finish |
| SPI D3 | Dry blast, rough textured finish |
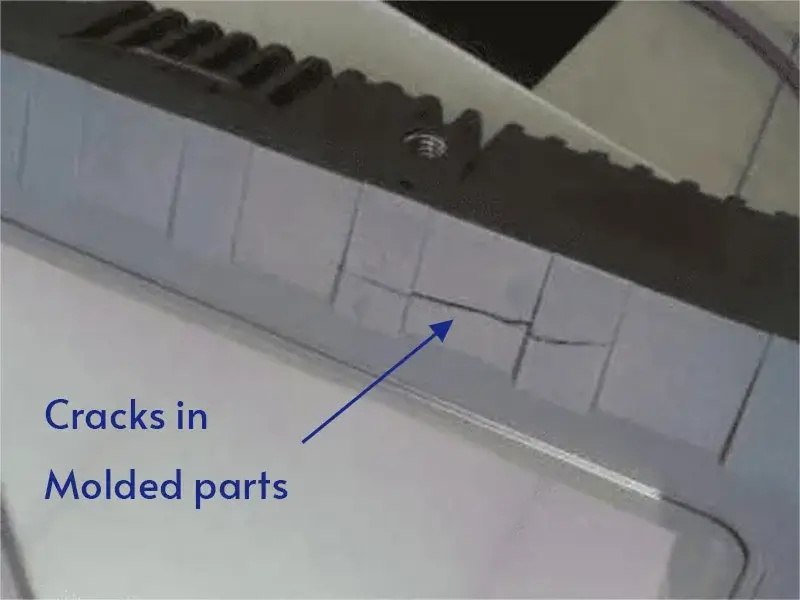
Understanding and Preventing Cracks in Molded Parts
How Does Compression Molding Work
Material Loading
Mold Closure and Heating
Compression and Curing
Cooling
Cycling
Advantages of Compression Molding
From intricate designs to high-volume production, compression olding stands out with its precision, efficiency, and adaptability.
- Cost-effective for large production runs due to its high prodcution output and reduced material waste.
- Ensures consistent part quality and minimal variation between parts in large batches.
- Well-suited for high-volume prodcution, contributing to faster lead times and efficient manufacturing processes.
- Minimized material waste, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing process.


Compression Molding Application
Compression molding produce a wide range of rubber and plastic molding parts across varios industries. Here are some common parts.
- Rubber seals and gaskets
- Plastic insulators for electrical components
- Rubber industrial bushings
- Consumer goods handles
- Plastic enclosures for electronic devices
- Oil seal
Why Choose Us
Ensuring accurate and intricate part production
Meeting diverse industry needs
Proven track record in successful projects
Rigorous quality checks for reliable results
Contract Manufacturing Solution

Mold & Tooling Service
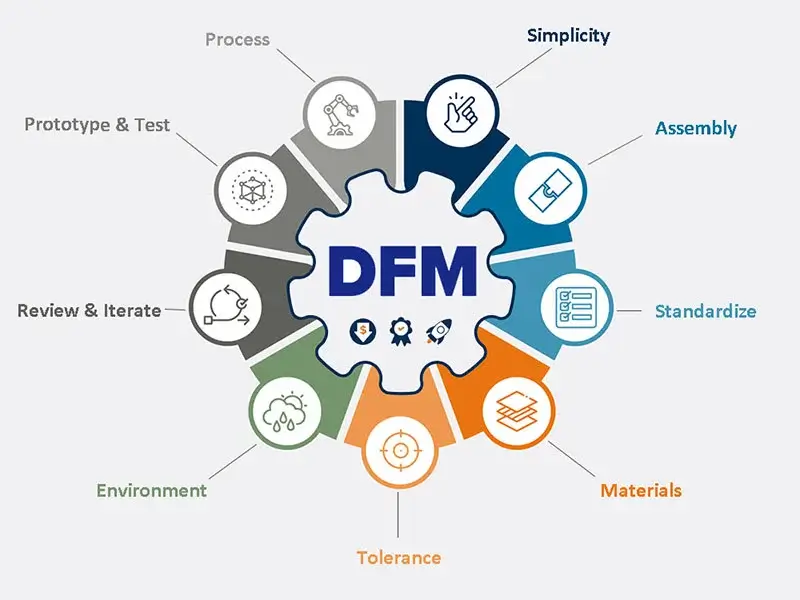
Design for Manufacturability

Surface Finishing

Assembly Manufacturing
FAQs of Compression Molding
What are the factores affecting compression molding?
Important factors to be considered before the compression molding process are the following:
- Amount of plastic material
- Heating time
- Melting temperature of plastic material
- The pressure required to squeeze the material into the mold cavity
- Cooling time
Is compression molding good for environment?
Compression moulding can help reduce the environmental impact of plastic production and disposal by minimizing waste and energy consumption and using recycle materials.
What is the cycle time of compression molding?
Compression molding require slower cycle time than injection molding, the time needed to start and repeat the sequence of operations is between 1-6 mins for compression molding.
Is compression molding cheaper than injection molding?
Injection molding is better suited to high-volume production, whereas compression molding is better suited to pliable and flexible materials. Generally, the upfront costs for compression molding are cheaper.